Pentagon Doesn’t Know What Happened to $1.3 Billion in Afghanistan

The Pentagon isn’t able to tell federal auditors what happened to more than $1.3 billion in funds intended for construction projects in Afghanistan.
The money was dispersed through a program established to speed up the rebuilding process in Afghanistan by giving money directly to military officers to build roads, bridges, dams and other projects to avoid the lengthy bureaucratic procurement process.
But in the rush to spend and build, much of the money paid out by the Commander’s Emergency Response Program (CERP) between 2004 and 2014 has gone unaccounted for, according to auditors who spent the last year trying to find it.
Related: 7 Threats to U.S. Rebuilding Efforts in Afghanistan
A new report released Friday by the Special Inspector General for Afghanistan Reconstruction says the Defense Department could only provide its office with documentation for $890 million, or roughly 40 percent, of the total $2.2 billion in funds.
The auditors blamed the Pentagon’s financial and project management process for not sufficiently tracking spending, saying DoD’s system doesn’t contain enough data or comprehensive information relating to the actual costs of the projects.
The auditors took the information the Pentagon did provide and divided it up into categories like education, health care, water and sanitation. Aside from transportation, the item that had the most expenses was labeled “unknown.”
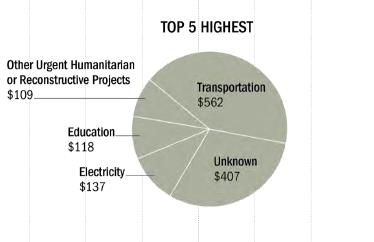
U.S. Central Command responded to the inspector general’s findings, or lack thereof, by saying that some of the unaccounted for CERP funds had been shifted to other military needs. “Although the report is technically accurate, it did not discuss the counterinsurgency strategies in relationship to CERP,” the Central Command said.
In total, the U.S. has doled out about $3.7 billion through CERP funds, with $2.2 billion coming from the Defense Department.
This is just the latest report from SIGAR highlighting the Pentagon’s problems keeping track of the enormous amount of money flowing into Afghanistan. Earlier reporting suggested the U.S. has lost some $100 billion in the reconstruction efforts.
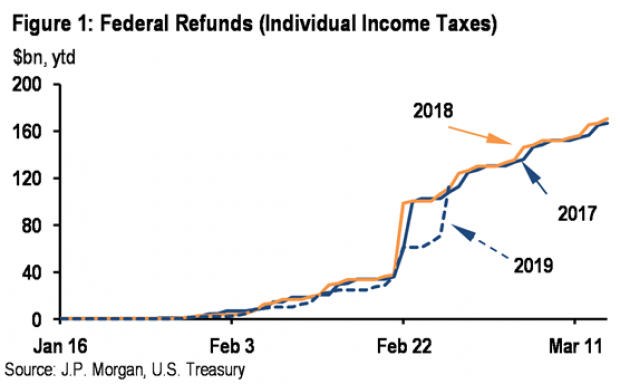
Tax Refunds Rebound

Smaller refunds in the first few weeks of the current tax season were shaping up to be a political problem for Republicans, but new data from the IRS shows that the value of refund checks has snapped back and is now running 1.3 percent higher than last year. The average refund through February 23 last year was $3,103, while the average refund through February 22 of 2019 was $3,143 – a difference of $40. The chart below from J.P. Morgan shows how refunds performed over the last 3 years.
Number of the Day: $22 Trillion

The total national debt surpassed $22 trillion on Monday. Total public debt outstanding reached $22,012,840,891,685.32, to be exact. That figure is up by more than $1.3 trillion over the past 12 months and by more than $2 trillion since President Trump took office.
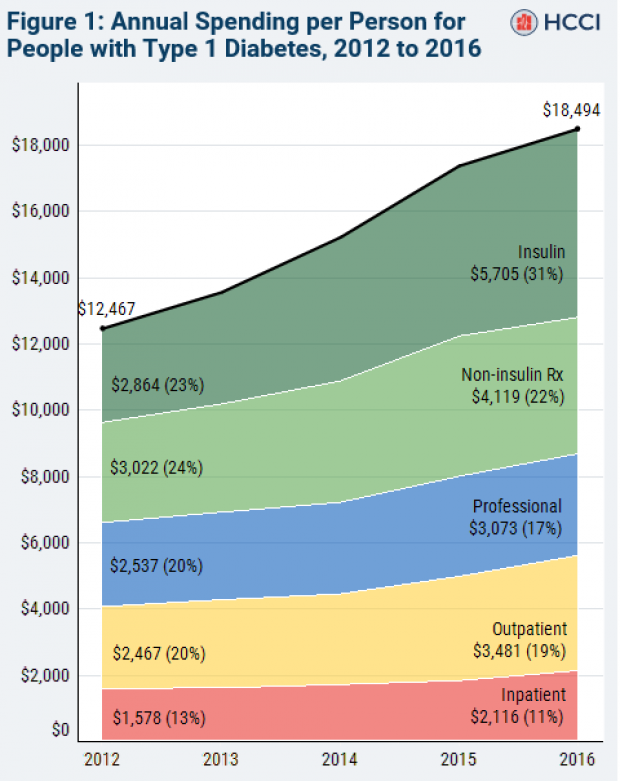
Chart of the Week: The Soaring Cost of Insulin
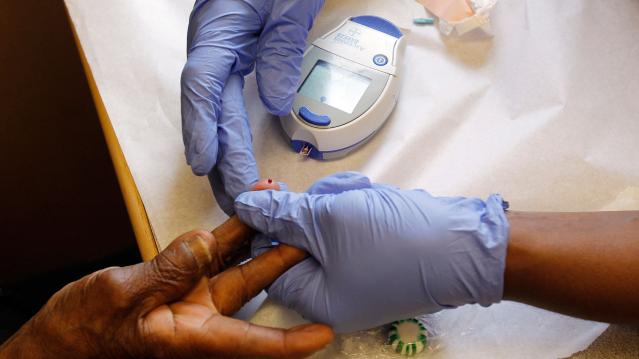
The cost of insulin used to treat Type 1 diabetes nearly doubled between 2012 and 2016, according to an analysis released this week by the Health Care Cost Institute. Researchers found that the average point-of-sale price increased “from $7.80 a day in 2012 to $15 a day in 2016 for someone using an average amount of insulin (60 units per day).” Annual spending per person on insulin rose from $2,864 to $5,705 over the five-year period. And by 2016, insulin costs accounted for nearly a third of all heath care spending for those with Type 1 diabetes (see the chart below), which rose from $12,467 in 2012 to $18,494.
Chart of the Day: Shutdown Hits Like a Hurricane

The partial government shutdown has hit the economy like a hurricane – and not just metaphorically. Analysts at the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget said Tuesday that the shutdown has now cost the economy about $26 billion, close to the average cost of $27 billion per hurricane calculated by the Congressional Budget Office for storms striking the U.S. between 2000 and 2015. From an economic point of view, it’s basically “a self-imposed natural disaster,” CRFB said.
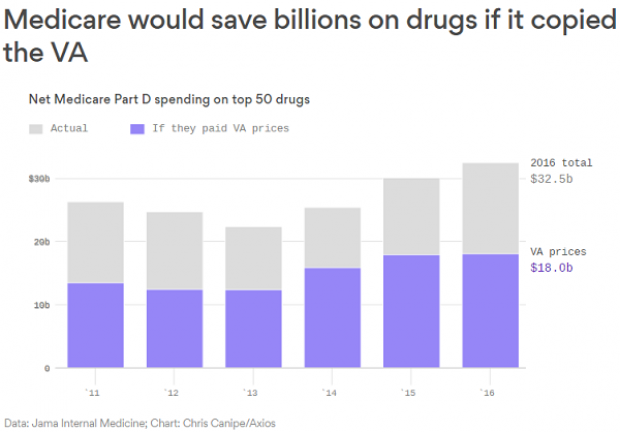
Chart of the Week: Lowering Medicare Drug Prices
The U.S. could save billions of dollars a year if Medicare were empowered to negotiate drug prices directly with pharmaceutical companies, according to a paper published by JAMA Internal Medicine earlier this week. Researchers compared the prices of the top 50 oral drugs in Medicare Part D to the prices for the same drugs at the Department of Veterans Affairs, which negotiates its own prices and uses a national formulary. They found that Medicare’s total spending was much higher than it would have been with VA pricing.
In 2016, for example, Medicare Part D spent $32.5 billion on the top 50 drugs but would have spent $18 billion if VA prices were in effect – or roughly 45 percent less. And the savings would likely be larger still, Axios’s Bob Herman said, since the study did not consider high-cost injectable drugs such as insulin.