Why the Rich Tend to Cheat on Their Brokers

For affluent Americans, having more than one financial adviser has now become the norm.
One in three Americans with more than $100,000 in investable assets started a relationship with a new financial services firm last year, seeking to combine the strengths of various firms to gain advice and resources, according to a new study released Tuesday by Hearts & Wallets, a financial research platform for consumers.
Related: The 6 Times You Really Need a Financial Adviser
Hearts & Wallets also noted that 55 percent of consumers with $500,000 in investable assets or more work with three or more firms.
Contrary to the popular image of wealthy investors dialing up their Wall Street broker, the Hearts & Wallets survey found that affluent investors are more likely to use self-service firms — discount brokerages like E*Trade or TD Ameritrade — than full-service brokers. More than 70 percent of investors with $500,000 or more use those self-service brokers, even if it’s for smaller “play money” accounts, compared with 40 percent for full-service firms such as Ameriprise and Edward Jones.
“It’s astonishing the self-service competitive set has deeper reach into investors with $500,000-plus, engaging more affluent investors than the full-service competitive set,” said Laura Varas, Hearts & Wallets partner and co-founder, in a press release.
Related: 6 Traits of an Emerging Millionaire: Are You One?
Some wealthy investors use both. A common pattern is what Hearts & Wallets calls “stable two-timing,” or when investors balance a self-service firm with a full-service firm. Some consumers might even tap into multiple high-service firms to obtain different advice.
“Just as in retail stores, wealthy customers may trust and frequent a Bloomingdale’s, but they will still shop at Costco, too,” Varas said. “Smart consumers compare.”
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- The 5 Worst Money Mistakes of Millionaires
- IRAs: Everything You Need to Know for 2015
- The Worst States For Retirement in 2015
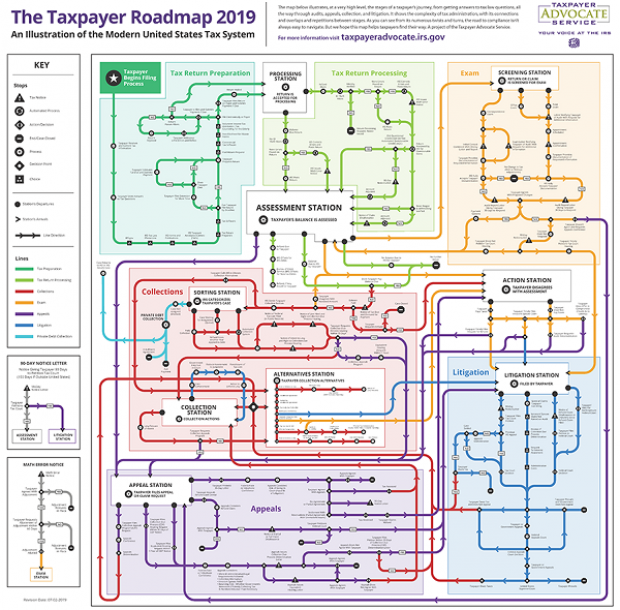
Map of the Day: Navigating the IRS

The Taxpayer Advocate Service – an independent organization within the IRS whose roughly 1,800 employees both assist taxpayers in resolving problems with the tax collection agency and recommend changes aimed at improving the system – released a “subway map” that shows the “the stages of a taxpayer’s journey.” The colorful diagram includes the steps a typical taxpayer takes to prepare and file their tax forms, as well as the many “stations” a tax return can pass through, including processing, audits, appeals and litigation. Not surprisingly, the map is quite complicated. Click here to review a larger version on the taxpayer advocate’s site.
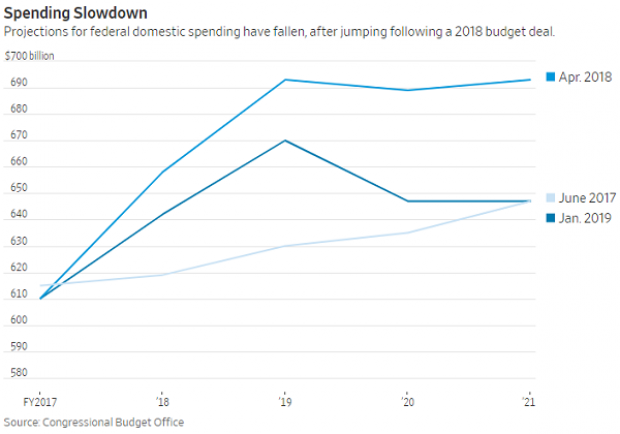
A Surprise Government Spending Slowdown

Economists expected federal spending to boost growth in 2019, but some of the fiscal stimulus provided by the 2018 budget deal has failed to show up this year, according to Kate Davidson of The Wall Street Journal.
Defense spending has come in as expected, but nondefense spending has lagged, and it’s unlikely to catch up to projections even if it accelerates in the coming months. Lower spending on disaster relief, the government shutdown earlier this year, and federal agencies spending less than they have been given by Congress all appear to be playing a role in the spending slowdown, Davidson said.
Number of the Day: $203,500

The Wall Street Journal’s Catherine Lucey reports that acting White House Chief of Staff Mick Mulvaney is making a bit more than his predecessors: “The latest annual report to Congress on White House personnel shows that President Trump’s third chief of staff is getting an annual salary of $203,500, compared with Reince Priebus and John Kelly, each of whom earned $179,700.” The difference is the result of Mulvaney still technically occupying the role of director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, where his salary level is set by law.
The White House told the Journal that if Mulvaney is made permanent chief of staff his salary would be adjusted to the current salary for an assistant to the president, $183,000.
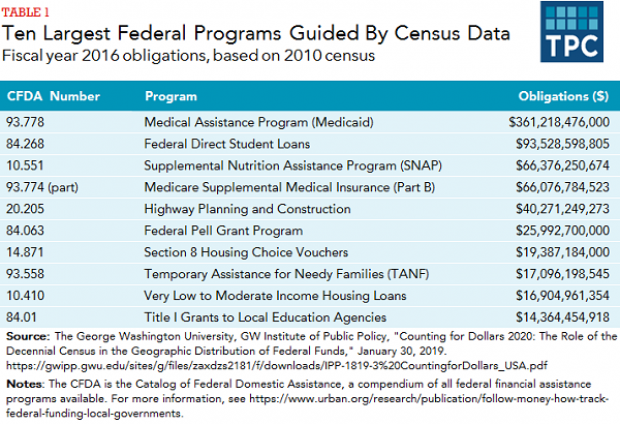
The Census Affects Nearly $1 Trillion in Spending

The 2020 census faces possible delay as the Supreme Court sorts out the legality of a controversial citizenship question added by the Trump administration. Tracy Gordon of the Tax Policy Center notes that in addition to the basic issue of political representation, the decennial population count affects roughly $900 billion in federal spending, ranging from Medicaid assistance funds to Section 8 housing vouchers. Here’s a look at the top 10 programs affected by the census:
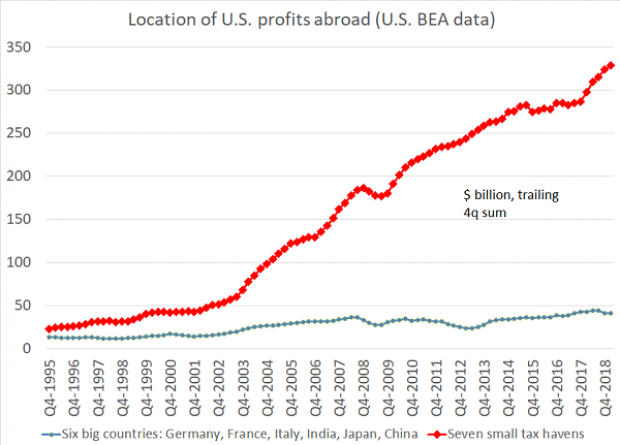
Chart of the Day: Offshore Profits Continue to Rise

Brad Setser, a former U.S. Treasury economist now with the Council on Foreign Relations, added another detail to his assessment of the foreign provisions of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act: “A bit more evidence that Trump's tax reform didn't change incentives to offshore profits: the enormous profits that U.S. firms report in low tax jurisdictions continues to rise,” Setser wrote. “In fact, there was a bit of a jump up over the course of 2018.”