Undertrained US Drone Pilots Put War Effort at Risk

The U.S. military is allowing pilots who haven’t fully completed their training to fly predator drones over Yemen and Pakistan—potentially putting innocent people on the ground at risk if something goes wrong.
An alarming new report by the Government Accountability Office found that drone pilots in the Army and Air Force have been skimping on their training sessions in order to get assigned to missions faster.
Related: Who Knew the Navy Could Launch 30 Drones in 60 Seconds?
The GAO said that because there is a shortage of drone pilots, the Air Force and Army have been routinely speeding up the process by cutting training time.
“As a result, the Army does not know the full extent to which pilots have been trained and are therefore ready to be deployed,” the report said.
The GAO reviewed Air Force records and found that only 35 percent of pilots operating drones had completed their required training.
Some pilots told the auditors that training wasn’t completed because there was a lack of funding or gaps in knowledge about the unmanned aerial systems (UAS) commonly called drones.
“Army UAS pilots stated that leadership of larger non-aviation units that oversee their UAS units do not understand UAS pilot training,” the report said.
The GAO had previously reported that there weren’t enough drone pilots compared with the number the Air Force said it needed. At New Mexico’s Holloman Air Force Base, for example, drone pilot staffing was at only 63 percent of full staffing level, the report said.
The latest findings from the GAO seem to confirm that this is still an issue.
Related: The Duck Drone That Could Change the Navy
The U.S. military says it is taking action to increase the number of instructors in order to get more pilots through the complete training process. However, the GAO said that the Army hasn’t fully addressed “the risks associated with using less experienced instructors.”
The Army waived course prerequisites for nearly 40 percent of its drone pilots who were working toward becoming instructors.
“As a result, the Army risks that its UAS pilots may not be receiving the highest caliber of training needed to prepare them to successfully perform UAS missions,” the auditors said.
Meanwhile the Air Force faces instructor shortages as well.
The report calls into question whether a lack of training could hamper drone pilots’ ability to successfully and safely complete their missions. It comes amid intense scrutiny of the government’s drone program after a botched mission in January killed two Western hostages during an attack on al Qaeda in Pakistan.
Scrutiny of the program is nothing new. Human rights activists have long called on the administration to cease using drones in its ongoing war on terror because of civilian casualties.
A 2013 report by Human Rights Watch said that between 2009 and 2013, U.S. drone strikes killed 57 civilians in six different strikes in Yemen. Last year the Yemeni government paid $1 million to families of victims of one of those strikes, which targeted a wedding and killed 11 people.
Number of the Day: $132,900

The cap on Social Security payroll taxes will rise to $132,900 next year, an increase of 3.5 percent. (Earnings up to that level are subject to the Social Security tax.) The increase will affect about 11.6 million workers, Politico reports. Beneficiaries are also getting a boost, with a 2.8 percent cost-of-living increase coming in 2019.
Photo of the Day: Kanye West at the White House

This is 2018: Kanye West visited President Trump at the White House Thursday and made a rambling 10-minute statement that aired on TV news networks. West’s lunch with the president was supposed to focus on clemency, crime in his hometown of Chicago and economic investment in urban areas, but his Oval Office rant veered into the bizarre. And since this is the world we live in, we’ll also point out that West apparently became “the first person to ever publicly say 'mother-f***er' in the Oval Office.”
Trump called Kanye’s monologue “pretty impressive.”
“That was bonkers,” MSNBC’s Ali Velshi said afterward.
Again, this is 2018.
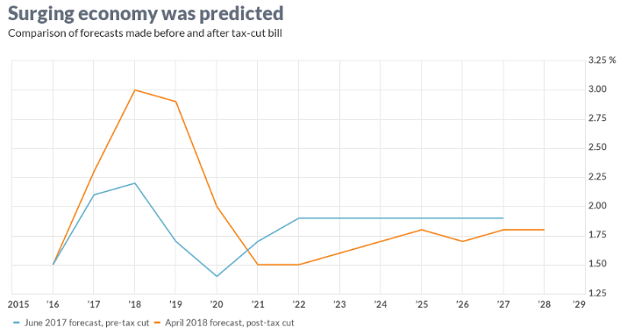
Chart of the Day: GDP Growth Before and After the Tax Bill

President Trump and the rest of the GOP are celebrating the recent burst in economic growth in the wake of the tax cuts, with the president claiming that it’s unprecedented and defies what the experts were predicting just a year ago. But Rex Nutting of MarketWatch points out that elevated growth rates over a few quarters have been seen plenty of times in recent years, and the extra growth generated by the Republican tax cuts was predicted by most economists, including those at the Congressional Budget Office, whose revised projections are shown below.
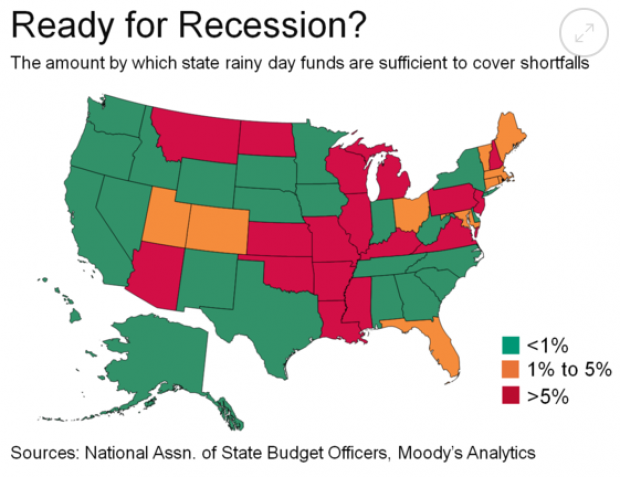
Are States Ready for the Next Downturn?

The Great Recession hit state budgets hard, but nearly half are now prepared to weather the next modest downturn. Moody’s Analytics says that 23 states have enough reserves to meet budget shortfalls in a moderate economic contraction, up from just 16 last year, Bloomberg reports. Another 10 states are close. The map below shows which states are within 1 percent of their funding needs for their rainy day funds (in green) and which states are falling short.
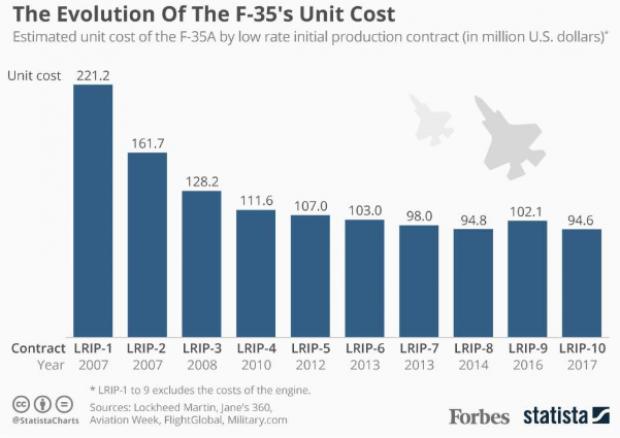
Chart of the Day: Evolving Price of the F-35

The 2019 National Defense Authorization Act signed in August included 77 F-35 Lightning II jets for the Defense Department, but Congress decided to bump up that number in the defense spending bill finalized this week, for a total of 93 in the next fiscal year – 16 more than requested by the Pentagon. Here’s a look from Forbes at the evolving per unit cost of the stealth jet, which is expected to eventually fall to roughly $80 million when full-rate production begins in the next few years.