The Amazingly Stupid Things Smartphone Users Do While Driving
If you’re reading this while driving, put your phone down right now. This article — as engrossing as it is — will still be here when you reach your destination.
We provide that friendly bit of advice because, as The New York Times reported this morning, a whole bunch of motorists are occupying themselves with their smartphones — and distracting themselves from the road — in ways that go way beyond talking and texting, according to a new survey conducted by Braun Research for AT&T.
The pollsters surveyed 2,067 smartphone users who drive daily, and their findings should be frightening to anyone on the roads. More than six in 10 smartphone users surveyed say they text while driving. It gets scarier: Nearly 40 percent of smartphone users admit to checking in on social media while driving, with 27 percent admitting to using Facebook and another 14 percent saying they use Twitter and Instagram while behind the wheel. Of users who cop to posting on Twitter while driving, 30 percent say they do it “all the time.” Given those figures, it’s amazing that #TwitterAccident isn’t always trending.
Related: Here's How Much Likelier You Are to Be Killed in a Car Than on Amtrak
Some other troubling stats from the survey: 17 percent snap selfies or other pictures when in the driver’s seat and 12 percent shoot videos — with 27 percent of those videographers thinking they can do so safely. Astoundingly, 10 percent of drivers say they video chat while on the roads.

AT&T says it will expand its It Can Wait public service campaign about the dangers of distracted driving, which launched in 2010, to focus on hazards beyond just texting. But as Matt Richtel of the Times points out, the AT&T campaign and other efforts like it face a stiff challenge in trying to counter the social pressures and strongly ingrained habits that keep people constantly checking their phones.
Tough laws and widespread educational efforts have been effective at reducing drunk driving and encouraging use of seat belts. But we still have a way to go in getting drivers to understand that “mobile” doesn’t mean when you’re behind the wheel. Right now, 46 states and the District of Columbia have outlawed texting while driving. As you can see above, that hasn't helped much yet. Smartphone users still need to be convinced of the danger they pose — or face — if they use their devices while driving.
As Lori Lee, AT&T’s global marketing officer, put it: “For the sake of you and those around you, please keep your eyes on the road, not on your phone.”
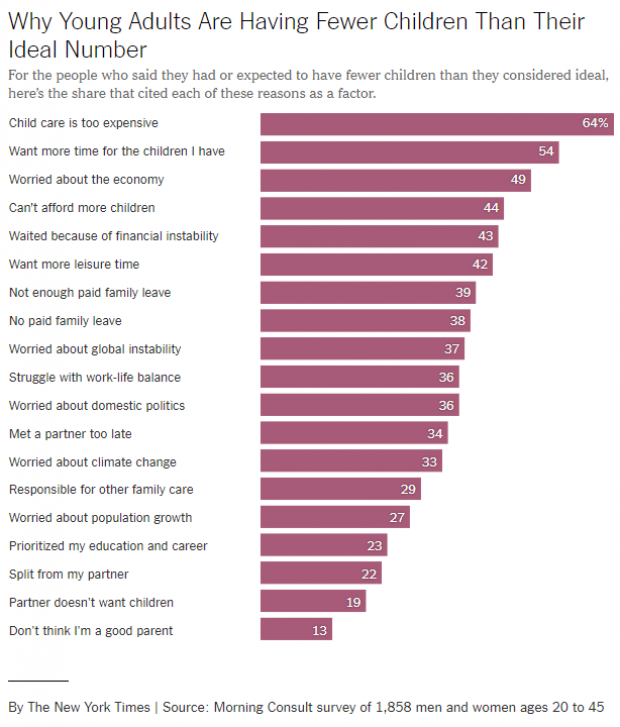
Chart of the Day: Why US Fertility Rates Are Falling

U.S. fertility rates have fallen to record lows for two straight years. “Because the fertility rate subtly shapes many major issues of the day — including immigration, education, housing, the labor supply, the social safety net and support for working families — there’s a lot of concern about why today’s young adults aren’t having as many children,” Claire Cain Miller explains at The New York Times’ Upshot. “So we asked them.”
Here are some results of the Times’ survey, conducted with Morning Consult. Read the full Times story for more details.
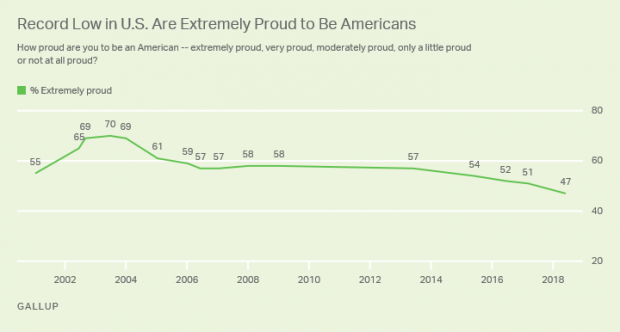
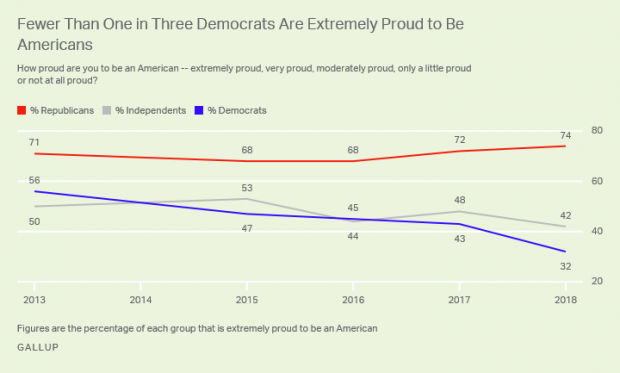
A Record Low 47% of US Adults Say They're 'Extremely Proud' to Be American
Gallup says that, for the first time in the 18 years it’s been asking U.S. adults how proud they are to be Americans, fewer than half say they are "extremely proud." Just 47 percent now say they’re extremely proud, down from 70 percent in 2003.
Another 25 percent say they’re “very proud” — but the combined 72 percent who say they’re extremely or very proud is also the lowest Gallup has recorded. Pride levels among liberals and Democrats have plunged since 2017. Overall, 74 percent of Republicans and just 32 percent of Democrats call themselves “extremely proud” to be American.
Pfizer Has Raised Prices on 100 of Its Products

Weeks after President Trump said that drugmakers were about to implement “voluntary massive drops in prices” — reductions that have yet to materialize — Pfizer has raised prices on 100 of its products, The Financial Times’s David Crow reports:
“The increases were effective as of July 1 and in most cases were more than 9 per cent — well above the rate of inflation in the US, which is running at about 2 per cent. … Pfizer, the largest standalone drugmaker in the US, did decrease the prices of five products by between 16 per cent and 44 per cent, according to the figures.”
Crow notes that Pfizer also raised prices on many of its medicines in January, meaning that some prices have been hiked by nearly 20 percent this year. The drugmaker said that it was only changing prices on 10 percent of its medicines and that list prices did not reflect what most patients or insurers actually paid. The net price increase after rebates and discounts was expected to be in the “low single digits,” the company told the FT.
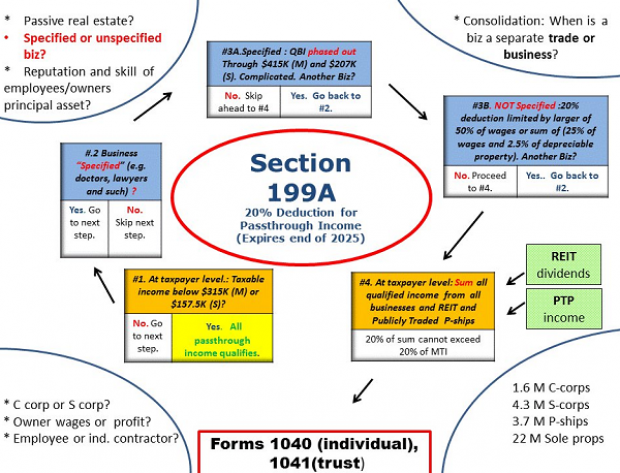
Chart of the Day: Pass-Through Tax Deductions Made Easy

The Republican tax overhaul was supposed to simplify the tax code, but most experts say it fell well short of the goal. Martin Sullivan, chief economist at Tax Analysts, tweeted out a chart of the analysis required to determine whether income qualifies for the passthrough tax deduction of 20 percent, and as you’ll see, it’s anything but simple.
A Conservative Bashes GOP Dysfunction on Spending Cuts

Brian Riedl, a senior fellow at the conservative Manhattan Institute, offers a blistering critique of congressional Republican’s problems cutting spending:
Since the Republicans took the House in 2011, nearly every annual budget blueprint has promised to balance the budget within a decade with anywhere from $5 trillion to $8 trillion in spending cuts. And yet, you may have noticed, the budget has not moved towards balance. This is because the budget merely sets a broad fiscal goal. To actually cut spending, Congress must follow up with specific legislation to reform Medicare, Medicaid, and all the other targeted programs. In reality, most lawmakers who pass these budgets have no intention whatsoever of cutting this spending. As soon as the budget is passed, the targets are forgotten. The spending-cut legislation is never even drafted, much less voted on.
The annual budget exercise is thus a cynical exercise in symbolism. Congress calculates how much spending must be cut over ten years to balance the budget. Then they pass legislation setting a goal of cutting that amount. Then they move on to other business. It’s like a baseball team announcing that they voted to win the next World Series, and then not showing up to play the season.
Read the full piece at National Review.