Obamacare’s Dirty Secret: 31 Million Still Can’t Afford Treatment
The president’s healthcare law sliced America’s uninsured rate down to historic lows by expanding coverage for tens of millions of Americans. At the same time, however, the number of insured people who still lack affordable, robust coverage is rising sharply as more people buy into high-deductible policies.
A new study from the Commonwealth Fund reveals that about 23 percent of Americans with coverage are considered underinsured—up from 12 percent in 2003. That means roughly 31 million Americans who bought health insurance still have trouble affording treatment under their policies.
The researchers at the Commonwealth Fund defined “underinsured” people as having out-of-pocket costs that total 10 percent or more of their annual income, or a deductible that is 5 percent or more of their income. The study concluded that high-deductible policies are likely the culprit behind this massive influx of underinsured people.
The findings are a huge problem for the Obama administration since the entire goal was to expand access to coverage to millions of Americans that they presumably would use instead of delaying treatment. But a handful of recent studies show that even people with health insurance are delaying treatment because they can’t afford it.
Related: High Deductible Plans Have More People Delaying Treatment
A December Gallup Poll showed at least 38 percent of insured, middle-income people, said they had delayed medical treatment because of the cost. “While many Americans have gained insurance, there has been no downturn in the percentage who say they have had to put off needed medical treatment because of cost,” Gallup’s Rebecca Riffkin wrote in a post on the pollster’s website.
The shift toward cost-sharing and high-deductible policies—defined by the Internal Revenue Service as those with annual deductibles of $1,300 or more for individuals and $2,600 for families--is widespread among exchange policies but also employer plans.
The Commonwealth Foundation’s study, unsurprisingly, reveals that low-income people with coverage are about twice as likely to be “underinsured” than people earning more than 200 percent of the poverty line.
Of course, it’s important to note that while affordability continues to be an issue, significantly more people do have health insurance because of the law.
Majority of Tax Cuts Going to Filers Earning More Than $100K: JCT

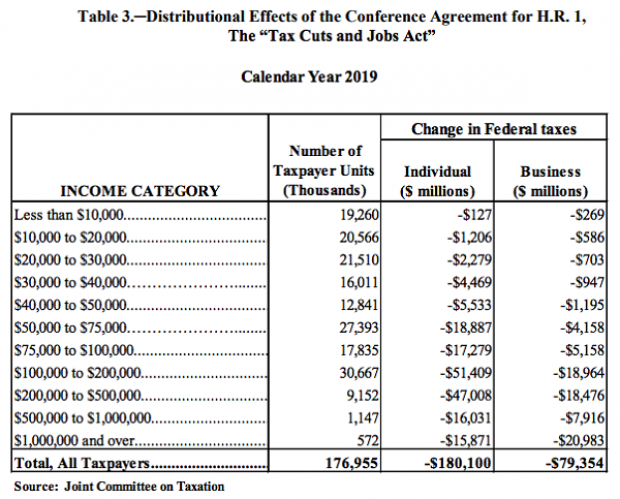
Ahead of a House Ways and Means Committee hearing scheduled for Wednesday, the Joint Committee on Taxation prepared an analysis of the distributional effects of the 2017 Republican tax bill. The New York Times’ Jim Tankersley highlighted the fact that according to the JCT analysis, about 75 percent of the individual and business benefits of the tax cuts will go to filers earning more than $100,000 in 2019. And nearly half of the benefits will flow to filers earning over $200,000.
The Trump Budget's $1.2 Trillion in 'Phantom Revenues'

President Trump’s 2020 budget includes up to $1.2 trillion in “potentially phantom revenues” — money that comes from taxes the administration opposes or from tax hikes that face strong opposition from businesses, The Wall Street Journal’s Richard Rubin reports, citing data from the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget. That total, covering 2020 through 2029, includes as much as $390 billion in taxes created under the Affordable Care Act, which the president wants to repeal.
The $1.2 trillion in questionable revenue projections is in addition to the White House budget’s projected deficits of $7.3 trillion for the 10-year period. That total is itself questionable, given that the president’s budget relies on optimistic assumptions about economic growth and some unrealistic spending cuts, meaning that the deficits could be significantly higher than projected.
Republicans Push Ahead on Medicaid Restrictions

The Trump administration on Friday approved Ohio’s request to impose work requirements on Medicaid recipients. Starting in 2021, the state will require most able-bodied adults aged 19 to 49 to either work, go to school, be in job training or volunteer for 80 hours a month in order to receive Medicaid benefits. Those who fail to meet the requirements over 60 days will be removed from the system, although they can reapply immediately.
The new work requirements include exemptions for pregnant women, caretakers and those living in counties with high unemployment rates and will apply only to those covered through the expansion of Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act. There are currently about 540,000 people on Medicaid in Ohio who receive coverage through the expansion, according to Kaitlin Schroeder of The Dayton Daily News, compared to roughly 2.6 million Medicaid recipients in the state overall.
Once implemented, the work requirements are expected to result in 36,000 people losing their Medicaid eligibility, according to state officials, though critics say the reductions could be significantly larger. Similar work requirements in Arkansas pushed 18,000 people off the Medicaid rolls in six months.
A larger GOP project: The creation of new work requirements is part of a larger effort by Republicans to limit the expansion of Medicaid, says The Wall Street Journal’s Stephanie Armour. Since the Affordable Care Act passed in 2010, 36 states have expanded their Medicaid programs under the ACA and the number of people in the program has grown by 50 percent, from roughly 50 million to about 75 million. But many red-state governors have expressed concerns about the cost of Medicaid expansion and worries about a lack of self-sufficiency among the able-bodied poor, and are embracing new limitations on the program for both fiscal and political reasons.
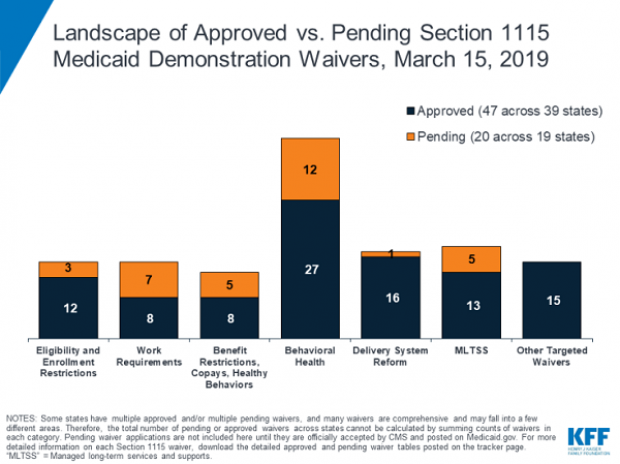
In 2017, the White House in 2017 gave states the green light to explore ways to limit the reach and expense of their Medicaid programs. Governors have proposed a variety of new rules, which require waivers from the federal government to enact. Kentucky, for example, wants to drug-test Medicaid recipients, and Utah wants a partial expansion and a cap on payments. Kaiser Health News summarizes the variety of waivers states have requested, which are governed by Section 1115 of the Social Security Act, in the chart below.
Legal challenges: Efforts to restrict Medicaid have received legal challenges, and U.S. District Judge James Boasberg blocked work requirements in Kentucky last year. The same judge, who has expressed doubts about the administration’s approach to Medicaid, will rule on the legality of work requirements in both Kentucky and Arkansas by April 1.
The bottom line: The Trump administration is seeking fundamental changes in how Medicaid works. Even if Boasberg rules against work requirements, expect the White House and Republican governors to continue to push for new limitations on the program.
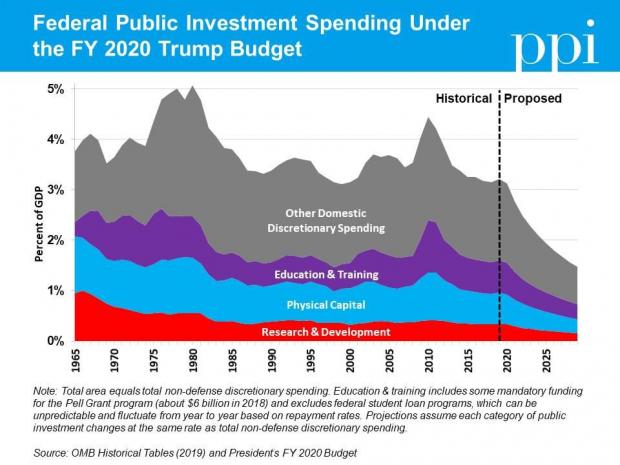
Chart of the Day: Trump's Huge Proposed Cuts to Public Investment

Ben Ritz of the Progressive Policy Institute slams President Trump’s new budget:
“It would dismantle public investments that lay the foundation for economic growth, resulting in less innovation. It would shred the social safety net, resulting in more poverty. It would rip away access to affordable health care, resulting in more disease. It would cut taxes for the rich, resulting in more income inequality. It would bloat the defense budget, resulting in more wasteful spending. And all this would add up to a higher national debt than the policies in President Obama’s final budget proposal.”
Here’s Ritz’s breakdown of Trump’s proposed spending cuts to public investment in areas such as infrastructure, education and scientific research:
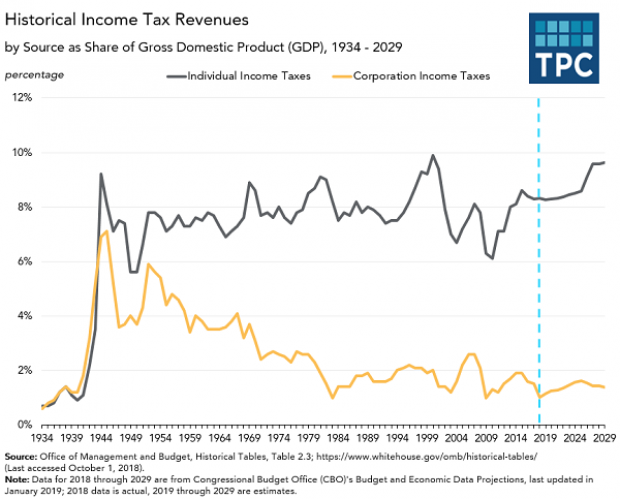
Chart of the Day: The Decline in Corporate Taxes

Since roughly the end of World War Two, individual income taxes in the U.S. have equaled about 8 percent of GDP. By contrast, the Tax Policy Center says, “corporate income tax revenues declined from 6% of GDP in 1950s to under 2% in the 1980s through the Great Recession, and have averaged 1.4% of GDP since then.”