The New Billionaires: Younger, Self-Made, More Diverse

Quick, picture a billionaire.
Chances are you conjured up an older, white man who inherited his fortune. That stereotype was pretty accurate for the past century, but times are changing.
Cultural and economic shifts over the past decade are realigning the demographics of the world’s 1 percent, and the billionaires of the future will be self-made, younger, and more diverse, according to a new report from UBS and PwC.
Last year, two-thirds of the world’s billionaires were self-made, compared with just 43 percent of billionaires 20 years ago. The report projects that the trend toward more self-made billionaires will continue get stronger over the next 5 to 10 years, peaking at about 70 percent of the billionaire population.
Related: Playgrounds of the Very Rich and Famous—A 2015 Guide
While two-thirds of current billionaires are over age 60, the average age is getting younger, thanks to both wealth transfers from the older generation and the growth of self-made billionaires.
In addition to getting younger, the report finds that billionaires are also increasingly more diverse. From 2003 to 2013, the number of female billionaires rose from 44 to 116. That’s still less than 10 percent, but it’s a number that’s growing fast.
Part of the trend toward diversity among billionaires is the explosive growth of wealth in Asia. In the first quarter of 2015, China created a new billionaire almost every week. The authors of the report expect that Asia will overtake the United States as the center of billionaire growth in the next decade.
Budget ‘Chaos’ Threatens Army Reset: Retired General
One thing is standing in the way of a major ongoing effort to reset the U.S. Army, writes Carter Ham, a retired four-star general who’s now president and CEO of the Association of the U.S. Army, at Defense One. “The problem is the Washington, D.C., budget quagmire.”
The issue is more than just a matter of funding levels. “What hurts more is the erratic, unreliable and downright harmful federal budget process,” which has forced the Army to plan based on stopgap “continuing resolutions” instead of approved budgets for nine straight fiscal years. “A slowdown in combat-related training, production delays in new weapons, and a postponement of increases in Army troop levels are among the immediate impacts of operating under this ill-named continuing resolution. It’s not continuous and it certainly doesn’t display resolve.”
Pentagon Pushes for Faster F-35 Cost Cuts

The Pentagon has taken over cost-cutting efforts for the F-35 program, which has been plagued by years of cost overruns, production delays and technical problems. The Defense Department rejected a cost-saving plan proposed by contractors including principal manufacturer Lockheed Martin as being too slow to produce substantial savings. Instead, it gave Lockheed a $60 million contract “to pursue further efficiency measures, with more oversight of how the money was spent,” The Wall Street Journal’s Doug Cameron reports. F-35 program leaders “say they want more of the cost-saving effort directed at smaller suppliers that haven’t been pressured enough.” The Pentagon plans to cut the price of the F-35A model used by the Air Force from a recent $94.6 million each to around $80 million by 2020. Overall, the price of developing the F-35 has climbed above $400 billion, with the total program cost now projected at $1.53 trillion. (Wall Street Journal, CNBC)
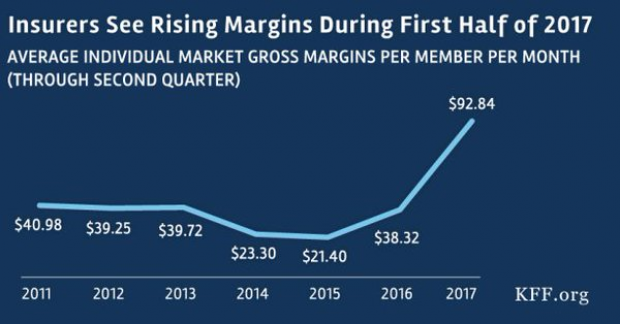
Chart of the Day - October 6, 2017
Financial performance for insurers in the individual Obamacare markets is improving, driven by higher premiums and slower growth in claims. This suggests that the market is stabilizing. (Kaiser Family Foundation)
Quote of the Day - October 5, 2017
"The train's left the station, and if you're a budget hawk, you were left at the station." -- Rep. Mark Sanford, R-S.C.