3 Dumb Moves That Can Hurt Your Career

What's the most common way to breach workplace etiquette and curb your career growth, if not derail it altogether?
AccountTemps says employers and staffers don't always see office etiquette the same. But bosses certainly have more leverage in the matter, since they can fire employees who buck the rules, and a company survey finds U.S. chief financial officers are most often bugged by workers "being distracted" on the job (27% of CFOs say so) and "gossiping about colleagues" (18%).
Other top offenses cited by CFOs:
- Not responding to calls or emails.
- Being late to meetings, or missing them.
- Not crediting other staffers when appropriate.
Employers and workers may not see the top etiquette breaches equally, but they agree on professional decorum more than they disagree, and the shared message is easy to sum up: "Most jobs today require teamwork and strong collaboration skills, and that means following the unwritten rules of office protocol," says Bill Driscoll, a district president of Accountemps. "Poor workplace etiquette demonstrates a lack of consideration for coworkers."
Related: Modern Etiquette: Outclassing the Competition
Of course, the list of workplace professional breaches exceeds the AccountTemps list.
"I've seen it all," notes Nicole Williams, a workplace consultant and a career contributor to NBC's The Today Show. "Employees who lie on expense reports; who badmouth the company or boss on social media or to clients; proofreading mistakes; missing deadlines. Just to name a few."
If you do trip up on the job, it's best to be accountable. "If you really screw up, you have to suffer the consequences in silence," Williams says. "Don't protest, don't try and get out of it, and don't put the blame on someone or something else. People will respect you more for owning your mistakes."
This article originally appeared on Main Street
Read More from Main Street
- 10 Ways to Blow a Job Interview
- The 10 Worst Cities to Enjoy a Summer 'Staycation'
- 12 Universities with the Biggest Endowments
Read more from Main Street: - See more at: http://www.thefiscaltimes.com/2015/05/19/Why-Even-Rich-Millennials-Are-F...
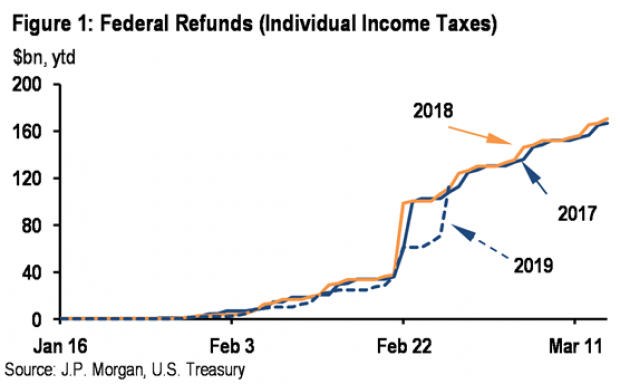
Tax Refunds Rebound

Smaller refunds in the first few weeks of the current tax season were shaping up to be a political problem for Republicans, but new data from the IRS shows that the value of refund checks has snapped back and is now running 1.3 percent higher than last year. The average refund through February 23 last year was $3,103, while the average refund through February 22 of 2019 was $3,143 – a difference of $40. The chart below from J.P. Morgan shows how refunds performed over the last 3 years.
Number of the Day: $22 Trillion

The total national debt surpassed $22 trillion on Monday. Total public debt outstanding reached $22,012,840,891,685.32, to be exact. That figure is up by more than $1.3 trillion over the past 12 months and by more than $2 trillion since President Trump took office.
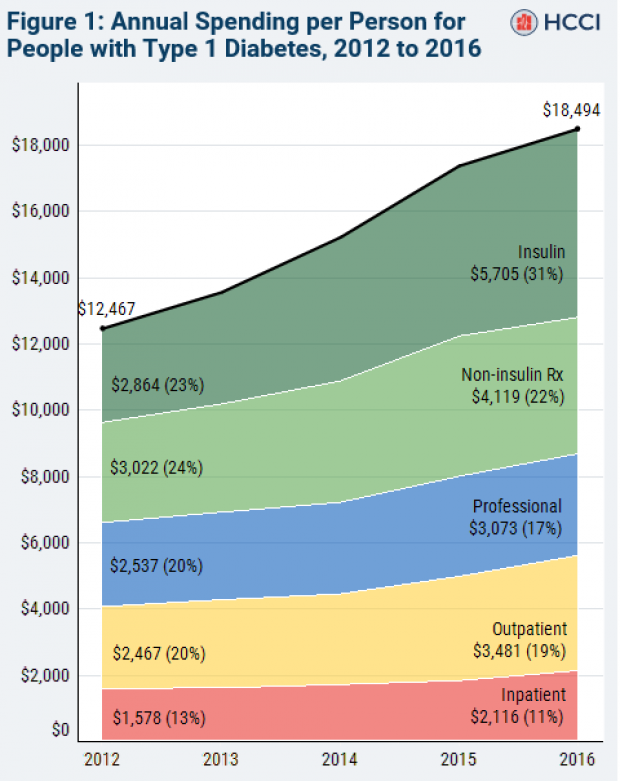
Chart of the Week: The Soaring Cost of Insulin
The cost of insulin used to treat Type 1 diabetes nearly doubled between 2012 and 2016, according to an analysis released this week by the Health Care Cost Institute. Researchers found that the average point-of-sale price increased “from $7.80 a day in 2012 to $15 a day in 2016 for someone using an average amount of insulin (60 units per day).” Annual spending per person on insulin rose from $2,864 to $5,705 over the five-year period. And by 2016, insulin costs accounted for nearly a third of all heath care spending for those with Type 1 diabetes (see the chart below), which rose from $12,467 in 2012 to $18,494.
Chart of the Day: Shutdown Hits Like a Hurricane

The partial government shutdown has hit the economy like a hurricane – and not just metaphorically. Analysts at the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget said Tuesday that the shutdown has now cost the economy about $26 billion, close to the average cost of $27 billion per hurricane calculated by the Congressional Budget Office for storms striking the U.S. between 2000 and 2015. From an economic point of view, it’s basically “a self-imposed natural disaster,” CRFB said.
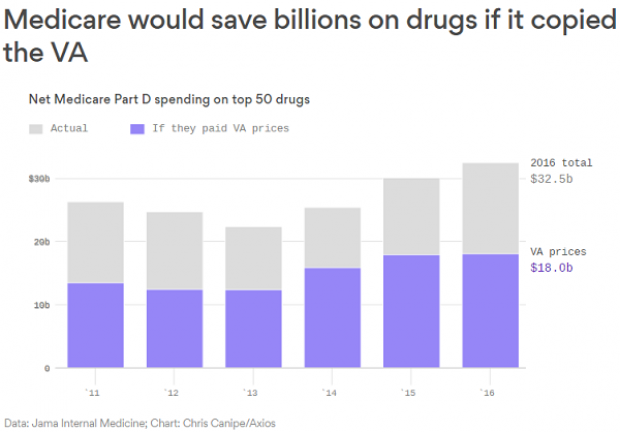
Chart of the Week: Lowering Medicare Drug Prices
The U.S. could save billions of dollars a year if Medicare were empowered to negotiate drug prices directly with pharmaceutical companies, according to a paper published by JAMA Internal Medicine earlier this week. Researchers compared the prices of the top 50 oral drugs in Medicare Part D to the prices for the same drugs at the Department of Veterans Affairs, which negotiates its own prices and uses a national formulary. They found that Medicare’s total spending was much higher than it would have been with VA pricing.
In 2016, for example, Medicare Part D spent $32.5 billion on the top 50 drugs but would have spent $18 billion if VA prices were in effect – or roughly 45 percent less. And the savings would likely be larger still, Axios’s Bob Herman said, since the study did not consider high-cost injectable drugs such as insulin.