Jamie Dimon Is Now a Billionaire

The vast majority of the billionaires in the U.S. made their money in one of two ways—they started a company, or they inherited their fortune or business.
But Jamie Dimon, chairman and CEO of JPMorgan Chase, has shown another path to riches. As a corporate manager, he may have amassed enough stock and boosted the share price enough to join the 10-figure club.
According to Bloomberg, Dimon is now worth $1.1 billion. His stake in JPMorgan through shares and options is worth $485 million and he also has real estate valued at $32 million. In addition, he has wealth from "an investment portfolio seeded by proceeds" from his previous stint at Citigroup.
Related: America’s Highest Paid CEO: It’s Not Who You Think
While highly unusual, Dimon isn't the first billionaire professional manager or executive who gained his wealth from stock in a company he didn't found or take public. The first manager-billionaire in the U.S. was believed to be Roberto Goizueta, CEO of Coca-Cola during the 1980s and 1990s. During his tenure, Coca-Cola's stock jumped more than 70-fold and Goizueta had stock and options totaling more than $1 billion.
More recently, the billionaire managers have been from finance. James Cayne, the colorful CEO and chairman of Bear Stearns became a billionaire on paper—before Bear Stearns collapsed during the financial crisis.
Richard Fuld, CEO of Lehman Brothers, also became a paper billionaire in 2007—before the investment bank became the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history in 2008.
Plenty of other finance chiefs have become billionaires—from hedge-funders to private-equity kings Steve Schwarzman and David Rubenstein. Citi founder Sandy Weill was a billionaire, but he created the company.
So while he may not be the first, Dimon may make history another way—by becoming the first manager-billionaire in finance to run a bank that thrives for decades after his leadership.
This article originally appeared on CNBC.
Read more from CNBc.
CNBC Charts the top 100 firms
Shift from slaes to planning fuels fee-only business
Harvard Receives Laegest Ever Gift
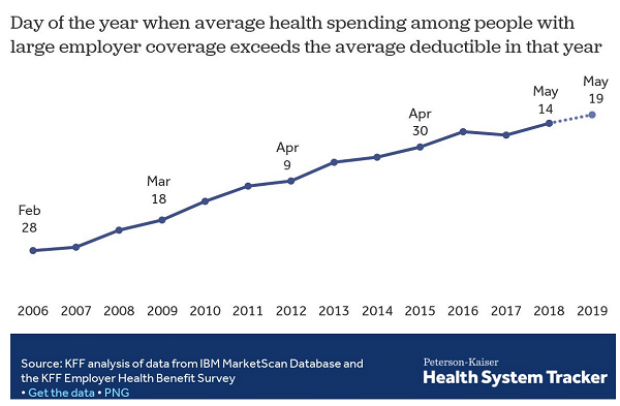
Coming Soon: Deductible Relief Day!

You may be familiar with the concept of Tax Freedom Day – the date on which you have earned enough to pay all of your taxes for the year. Focusing on a different kind of financial burden, analysts at the Kaiser Family Foundation have created Deductible Relief Day – the date on which people in employer-sponsored insurance plans have spent enough on health care to meet the average annual deductible.
Average deductibles have more than tripled over the last decade, forcing people to spend more out of pocket each year. As a result, Deductible Relief Day is “getting later and later in the year,” Kaiser’s Larry Levitt said in a tweet Thursday.
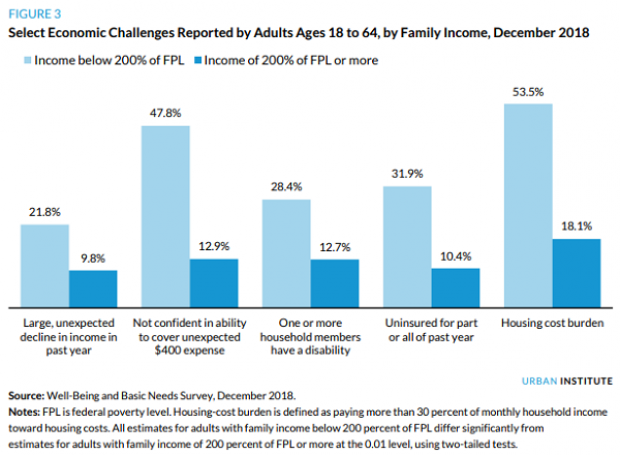
Chart of the Day: Families Still Struggling

Ten years into what will soon be the longest economic expansion in U.S. history, 40% of families say they are still struggling, according to a new report from the Urban Institute. “Nearly 4 in 10 nonelderly adults reported that in 2018, their families experienced material hardship—defined as trouble paying or being unable to pay for housing, utilities, food, or medical care at some point during the year—which was not significantly different from the share reporting these difficulties for the previous year,” the report says. “Among adults in families with incomes below twice the federal poverty level (FPL), over 60 percent reported at least one type of material hardship in 2018.”
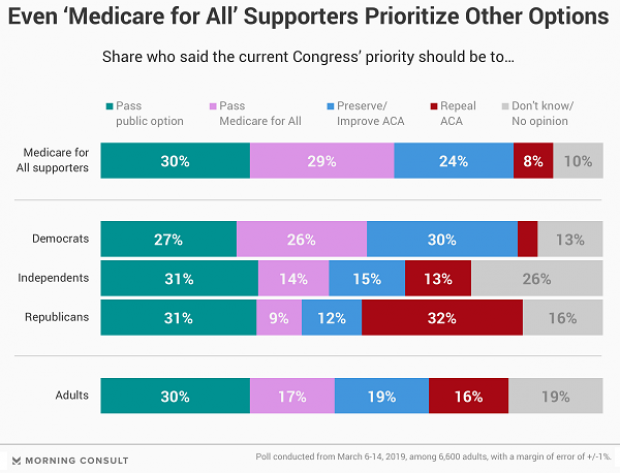
Chart of the Day: Pragmatism on a Public Option

A recent Morning Consult poll 3,073 U.S. adults who say they support Medicare for All shows that they are just as likely to back a public option that would allow Americans to buy into Medicare or Medicaid without eliminating private health insurance. “The data suggests that, in spite of the fervor for expanding health coverage, a majority of Medicare for All supporters, like all Americans, are leaning into their pragmatism in response to the current political climate — one which has left many skeptical that Capitol Hill can jolt into action on an ambitious proposal like Medicare for All quickly enough to wrangle the soaring costs of health care,” Morning Consult said.
Chart of the Day: The Explosive Growth of the EITC

The Earned Income Tax Credit, a refundable tax credit for low- to moderate-income workers, was established in 1975, with nominal claims of about $1.2 billion ($5.6 billion in 2016 dollars) in its first year. According to the Tax Policy Center, by 2016 “the total was $66.7 billion, almost 12 times larger in real terms.”
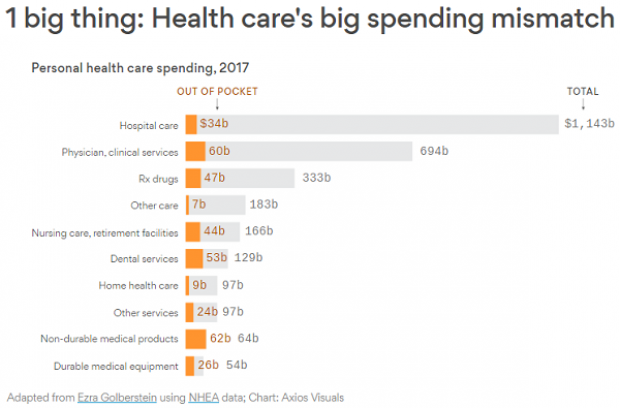
Chart of the Day: The Big Picture on Health Care Costs

“The health care services that rack up the highest out-of-pocket costs for patients aren't the same ones that cost the most to the health care system overall,” says Axios’s Caitlin Owens. That may distort our view of how the system works and how best to fix it. For example, Americans spend more out-of-pocket on dental services ($53 billion) than they do on hospital care ($34 billion), but the latter is a much larger part of national health care spending as a whole.