Obama Says King v. Burwell Is an ‘Easy Case’

House Republicans are gearing up to grill Health and Human Services Secretary Sylvia Mathews Burwell this week over how the administration will handle any potential fallout if the Supreme Court strikes down federal subsidies for health insurance coverage in 34 states operating on the federal exchange. Burwell will testify before the House Ways and Means Committee on Wednesday, ahead of the high court’s ruling in the high-stakes case of King v. Burwell, expected later this month.
The plaintiffs in that case contend that the law’s language only provides for subsidies to people in states that created their own exchange. The Obama administration and authors of the law maintain that the law was intended to offer subsidies to all enrollees who are eligible based on their income regardless of which exchange they used.
Related: If Obamacare Collapses, These 9 Ideas Could Save Health Care
If the court rules against the administration, an estimated 6.5 million people could lose their subsidized health coverage. If that happens, experts say it could create a ripple effect throughout health insurance markets in federal exchange states. Nearly everyone agrees that such a ruling would be devastating for millions of Americans. However, there is little agreement over what, if anything, to do to stem such fallout if the court rules for the plaintiffs.
Asked why his administration has given little guidance to states on how to prepare for the potential loss of federal insurance subsidies, President Obama on Monday said, “there is no reason why the existing exchanges should be overturned through a court case.”
King v. Burwell “should be an easy case,” Obama said. “Frankly, it probably shouldn’t even have been taken up. And since we’re going to get a ruling pretty quick, I think it’s important for us to go ahead and assume that the Supreme Court is going to do what most legal scholars who’ve looked at this would expect them to do.”
Obama added that Congress could also resolve any problems raised by a court ruling “with a one-sentence provision.”
Related: Double Digit Rate Hikes Loom for Obamacare 2016
That kind of response is unlikely to satisfy House Republicans, who are likely to again question Burwell’s previous claims that the administration does not have a “Plan B” in place if the court strikes down federal subsidies for millions of Americans.
Last week, during a Wall Street Journal breakfast, Burwell explained that the administration’s authority is limited. She added that her agency would work with states that are considering creating their own exchanges or using workarounds to avoid losing out on the federal subsidies.
“As always, we will stand ready to work with states, but in terms of administrative authority, we can’t do much,” Burwell said.
Republicans, who have long sought to repeal Obamacare, have criticized the administration for not having a contingency plan in place if the subsidies get struck down.
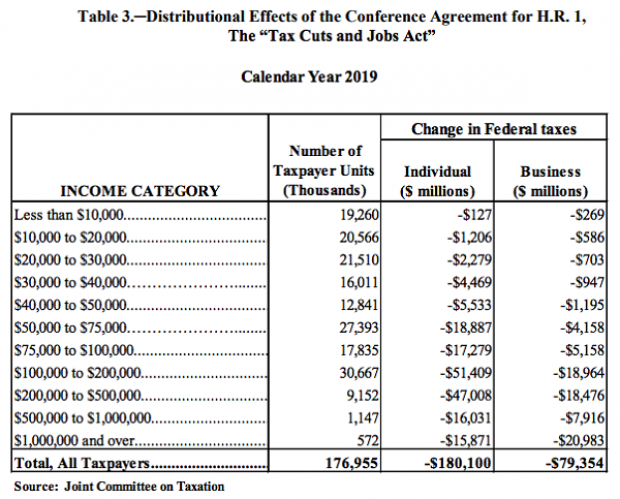
Majority of Tax Cuts Going to Filers Earning More Than $100K: JCT

Ahead of a House Ways and Means Committee hearing scheduled for Wednesday, the Joint Committee on Taxation prepared an analysis of the distributional effects of the 2017 Republican tax bill. The New York Times’ Jim Tankersley highlighted the fact that according to the JCT analysis, about 75 percent of the individual and business benefits of the tax cuts will go to filers earning more than $100,000 in 2019. And nearly half of the benefits will flow to filers earning over $200,000.
The Trump Budget's $1.2 Trillion in 'Phantom Revenues'

President Trump’s 2020 budget includes up to $1.2 trillion in “potentially phantom revenues” — money that comes from taxes the administration opposes or from tax hikes that face strong opposition from businesses, The Wall Street Journal’s Richard Rubin reports, citing data from the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget. That total, covering 2020 through 2029, includes as much as $390 billion in taxes created under the Affordable Care Act, which the president wants to repeal.
The $1.2 trillion in questionable revenue projections is in addition to the White House budget’s projected deficits of $7.3 trillion for the 10-year period. That total is itself questionable, given that the president’s budget relies on optimistic assumptions about economic growth and some unrealistic spending cuts, meaning that the deficits could be significantly higher than projected.
Republicans Push Ahead on Medicaid Restrictions

The Trump administration on Friday approved Ohio’s request to impose work requirements on Medicaid recipients. Starting in 2021, the state will require most able-bodied adults aged 19 to 49 to either work, go to school, be in job training or volunteer for 80 hours a month in order to receive Medicaid benefits. Those who fail to meet the requirements over 60 days will be removed from the system, although they can reapply immediately.
The new work requirements include exemptions for pregnant women, caretakers and those living in counties with high unemployment rates and will apply only to those covered through the expansion of Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act. There are currently about 540,000 people on Medicaid in Ohio who receive coverage through the expansion, according to Kaitlin Schroeder of The Dayton Daily News, compared to roughly 2.6 million Medicaid recipients in the state overall.
Once implemented, the work requirements are expected to result in 36,000 people losing their Medicaid eligibility, according to state officials, though critics say the reductions could be significantly larger. Similar work requirements in Arkansas pushed 18,000 people off the Medicaid rolls in six months.
A larger GOP project: The creation of new work requirements is part of a larger effort by Republicans to limit the expansion of Medicaid, says The Wall Street Journal’s Stephanie Armour. Since the Affordable Care Act passed in 2010, 36 states have expanded their Medicaid programs under the ACA and the number of people in the program has grown by 50 percent, from roughly 50 million to about 75 million. But many red-state governors have expressed concerns about the cost of Medicaid expansion and worries about a lack of self-sufficiency among the able-bodied poor, and are embracing new limitations on the program for both fiscal and political reasons.
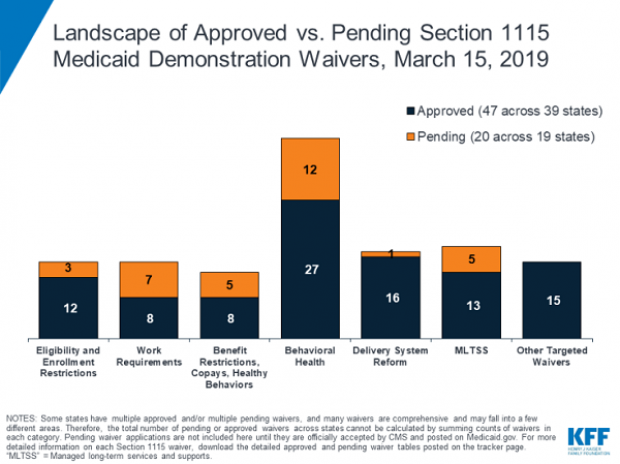
In 2017, the White House in 2017 gave states the green light to explore ways to limit the reach and expense of their Medicaid programs. Governors have proposed a variety of new rules, which require waivers from the federal government to enact. Kentucky, for example, wants to drug-test Medicaid recipients, and Utah wants a partial expansion and a cap on payments. Kaiser Health News summarizes the variety of waivers states have requested, which are governed by Section 1115 of the Social Security Act, in the chart below.
Legal challenges: Efforts to restrict Medicaid have received legal challenges, and U.S. District Judge James Boasberg blocked work requirements in Kentucky last year. The same judge, who has expressed doubts about the administration’s approach to Medicaid, will rule on the legality of work requirements in both Kentucky and Arkansas by April 1.
The bottom line: The Trump administration is seeking fundamental changes in how Medicaid works. Even if Boasberg rules against work requirements, expect the White House and Republican governors to continue to push for new limitations on the program.
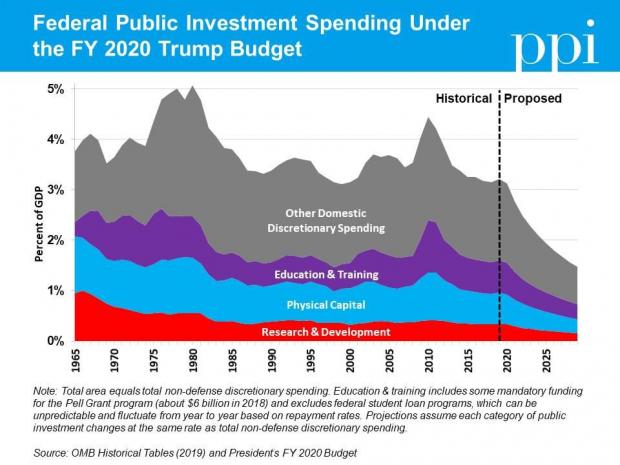
Chart of the Day: Trump's Huge Proposed Cuts to Public Investment

Ben Ritz of the Progressive Policy Institute slams President Trump’s new budget:
“It would dismantle public investments that lay the foundation for economic growth, resulting in less innovation. It would shred the social safety net, resulting in more poverty. It would rip away access to affordable health care, resulting in more disease. It would cut taxes for the rich, resulting in more income inequality. It would bloat the defense budget, resulting in more wasteful spending. And all this would add up to a higher national debt than the policies in President Obama’s final budget proposal.”
Here’s Ritz’s breakdown of Trump’s proposed spending cuts to public investment in areas such as infrastructure, education and scientific research:
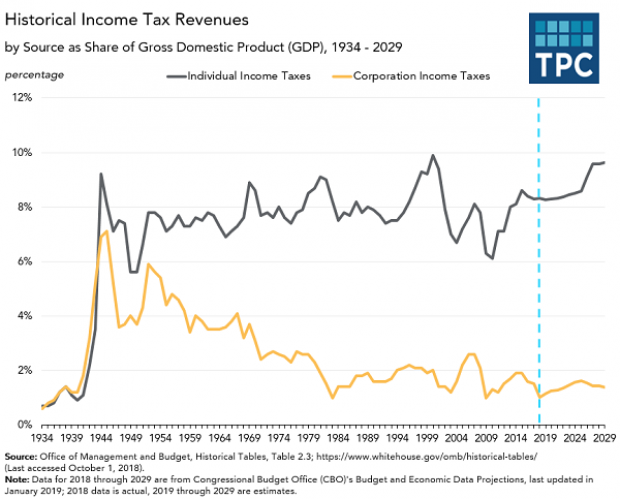
Chart of the Day: The Decline in Corporate Taxes

Since roughly the end of World War Two, individual income taxes in the U.S. have equaled about 8 percent of GDP. By contrast, the Tax Policy Center says, “corporate income tax revenues declined from 6% of GDP in 1950s to under 2% in the 1980s through the Great Recession, and have averaged 1.4% of GDP since then.”