Why Your Next Phone Could Be Powered By Seawater

Lithium is more than just a pretty solid Nirvana track – it’s also the reason that the portable computer in your pocket can keep on tweeting, e-mailing and otherwise vibrating for hours on end.
But soon there may not be enough available to go around.
As the demand for long-lasting batteries in cell-phones, laptops, and electric cars increases, so too does demand for Lithium, their key ingredient.
The U.S. Geological Survey estimated recently that conventional lithium reserves provide enough for production of 37,000 tons of the element per year for 365 years. That sounds like a lot, but with over a million electric cars expected in 2020, the development of battery clusters that power smart homes (like Tesla’s Powerwall), and increasing availability of lithium-powered consumer electronics, demand is sure to rise exponentially every year.
To battle the problem of Lithium shortage, researchers are looking to some unconventional sources. In Japan, for instance, scientists at the Atomic Energy Agency are working on a method to extract lithium from seawater through dialysis. According to a report from MIT Technology Review, “The system is based on a dialysis cell with a membrane consisting of a superconductor material,” a sentence which presumably means something to someone, somewhere.
Though the method is a long way away from being used commercially, one of the lead scientists on the project, Tsuyoshi Hoshino wrote that this particular method of extracting Lithium “shows good energy efficiency and is easily scalable.” Hoshino adds that his method could be commercialized in five years.
If Hoshino’s method makes it to commercialization, it could be a huge boom for the lithium battery industry, especially to powerhouse Tesla. Mineral assays of Nevada’s salt lakes have shown promising concentrations of lithium, which also happens to be where the battery pioneer plans to build its massive battery production plant, known as the “Gigafactory.”
For now, though, we’re stuck with a reliance on more conventional lithium sources.
Number of the Day: $132,900

The cap on Social Security payroll taxes will rise to $132,900 next year, an increase of 3.5 percent. (Earnings up to that level are subject to the Social Security tax.) The increase will affect about 11.6 million workers, Politico reports. Beneficiaries are also getting a boost, with a 2.8 percent cost-of-living increase coming in 2019.
Photo of the Day: Kanye West at the White House

This is 2018: Kanye West visited President Trump at the White House Thursday and made a rambling 10-minute statement that aired on TV news networks. West’s lunch with the president was supposed to focus on clemency, crime in his hometown of Chicago and economic investment in urban areas, but his Oval Office rant veered into the bizarre. And since this is the world we live in, we’ll also point out that West apparently became “the first person to ever publicly say 'mother-f***er' in the Oval Office.”
Trump called Kanye’s monologue “pretty impressive.”
“That was bonkers,” MSNBC’s Ali Velshi said afterward.
Again, this is 2018.
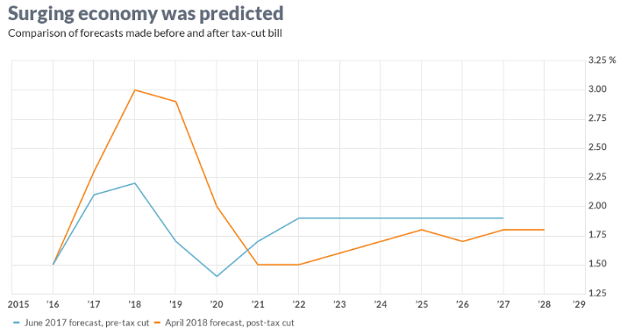
Chart of the Day: GDP Growth Before and After the Tax Bill

President Trump and the rest of the GOP are celebrating the recent burst in economic growth in the wake of the tax cuts, with the president claiming that it’s unprecedented and defies what the experts were predicting just a year ago. But Rex Nutting of MarketWatch points out that elevated growth rates over a few quarters have been seen plenty of times in recent years, and the extra growth generated by the Republican tax cuts was predicted by most economists, including those at the Congressional Budget Office, whose revised projections are shown below.
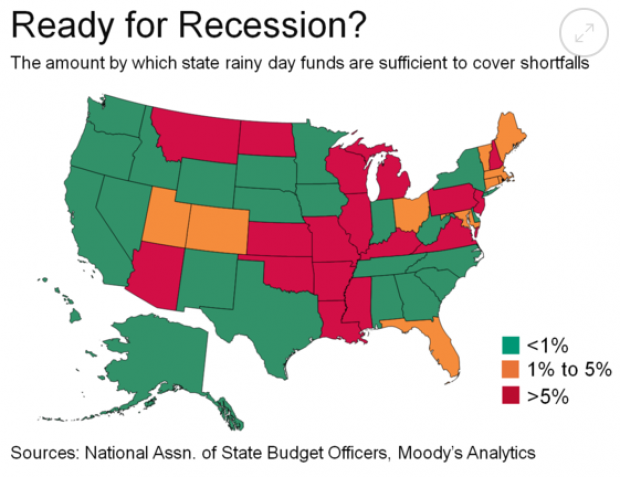
Are States Ready for the Next Downturn?

The Great Recession hit state budgets hard, but nearly half are now prepared to weather the next modest downturn. Moody’s Analytics says that 23 states have enough reserves to meet budget shortfalls in a moderate economic contraction, up from just 16 last year, Bloomberg reports. Another 10 states are close. The map below shows which states are within 1 percent of their funding needs for their rainy day funds (in green) and which states are falling short.
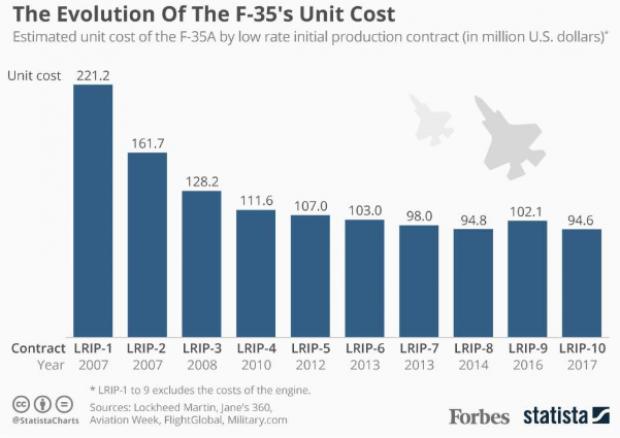
Chart of the Day: Evolving Price of the F-35

The 2019 National Defense Authorization Act signed in August included 77 F-35 Lightning II jets for the Defense Department, but Congress decided to bump up that number in the defense spending bill finalized this week, for a total of 93 in the next fiscal year – 16 more than requested by the Pentagon. Here’s a look from Forbes at the evolving per unit cost of the stealth jet, which is expected to eventually fall to roughly $80 million when full-rate production begins in the next few years.