VA Cited for Neglecting Follow-Up Treatment for Depressed Vets

The embattled Veterans Affairs Department is once again under scrutiny for potentially violating agency guidelines when treating patients—this time, failing to ensure that veterans with depression are receiving sufficient follow-up care after being prescribed anti-depressant medication.
That’s the conclusion of an investigation by the Government Accountability Office. The GAO reviewed patients being treated for depression at six separate VA medical centers and found that after the veterans received anti-depressants, their doctors did not conduct follow-up appointments within four to six weeks, as the VA requires
Related: VA Wastes Millions, But Still Wants More as Vets Wait for Care
In its review, the GAO said that among all patients whose records were reviewed—almost none of them received check ups with doctors in the required time after they were given anti-depressant medication.
"Given the debilitating effect that depression can have on veterans' quality of life, VA's monitoring of veterans with [depression] is critical to ensuring they receive care that is associated with positive health care outcomes," GAO director of health care Randall Williamson said in congressional testimony this week. He went on to criticize the VA for not following its own guidelines to assure veterans receive sufficient treatment.
“This work illustrates, once again, a continuing pattern of VHA's [Veterans Health Administration] noncompliance with its own policies and established procedures,” Randall Williamson, the GAO's director of health care said in congressional testimony last week.
Separately, the GAP flagged the VA’s Behavioral Health Autopsy Program which is used to collect data on veterans that have committed suicide in order to inform policy decisions, saying it is plagued with inaccuracies.
Auditors said that the system had incorrect dates of death—sometimes off by one day, sometimes off by a whole year. The GAO said this made it nearly impossible to assess what kind of treatment they were provided.
Number of the Day: $132,900

The cap on Social Security payroll taxes will rise to $132,900 next year, an increase of 3.5 percent. (Earnings up to that level are subject to the Social Security tax.) The increase will affect about 11.6 million workers, Politico reports. Beneficiaries are also getting a boost, with a 2.8 percent cost-of-living increase coming in 2019.
Photo of the Day: Kanye West at the White House

This is 2018: Kanye West visited President Trump at the White House Thursday and made a rambling 10-minute statement that aired on TV news networks. West’s lunch with the president was supposed to focus on clemency, crime in his hometown of Chicago and economic investment in urban areas, but his Oval Office rant veered into the bizarre. And since this is the world we live in, we’ll also point out that West apparently became “the first person to ever publicly say 'mother-f***er' in the Oval Office.”
Trump called Kanye’s monologue “pretty impressive.”
“That was bonkers,” MSNBC’s Ali Velshi said afterward.
Again, this is 2018.
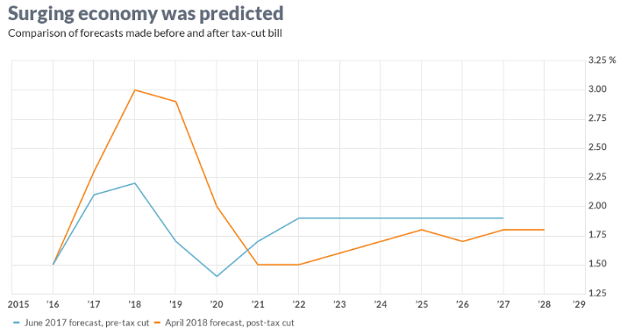
Chart of the Day: GDP Growth Before and After the Tax Bill

President Trump and the rest of the GOP are celebrating the recent burst in economic growth in the wake of the tax cuts, with the president claiming that it’s unprecedented and defies what the experts were predicting just a year ago. But Rex Nutting of MarketWatch points out that elevated growth rates over a few quarters have been seen plenty of times in recent years, and the extra growth generated by the Republican tax cuts was predicted by most economists, including those at the Congressional Budget Office, whose revised projections are shown below.
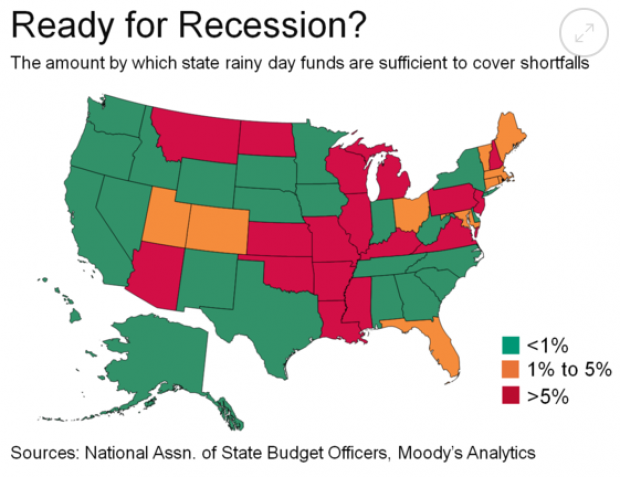
Are States Ready for the Next Downturn?

The Great Recession hit state budgets hard, but nearly half are now prepared to weather the next modest downturn. Moody’s Analytics says that 23 states have enough reserves to meet budget shortfalls in a moderate economic contraction, up from just 16 last year, Bloomberg reports. Another 10 states are close. The map below shows which states are within 1 percent of their funding needs for their rainy day funds (in green) and which states are falling short.
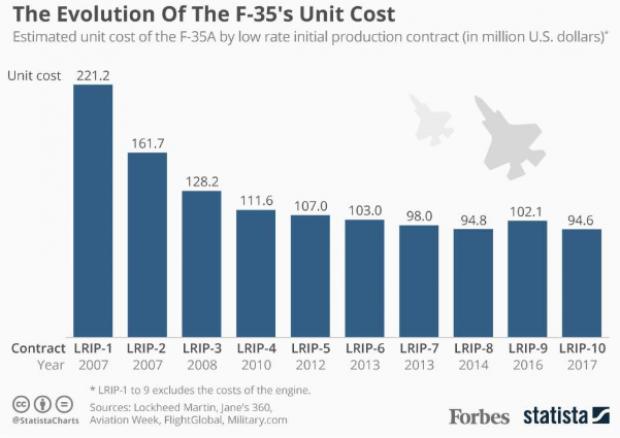
Chart of the Day: Evolving Price of the F-35

The 2019 National Defense Authorization Act signed in August included 77 F-35 Lightning II jets for the Defense Department, but Congress decided to bump up that number in the defense spending bill finalized this week, for a total of 93 in the next fiscal year – 16 more than requested by the Pentagon. Here’s a look from Forbes at the evolving per unit cost of the stealth jet, which is expected to eventually fall to roughly $80 million when full-rate production begins in the next few years.