It’s Not Just in Your Head, the Web Is Slowing Down

It’s not your imagination, and it’s not because AT&T — and possibly others — is purposefully cutting speeds to unlimited data plan users. The Internet is slowing down. The reason: Websites are growing in size, causing slower load times.
The average website is now 2.1 MB in size, compared to 1.5 MB two years ago, according to HTTP Archive, an Internet data measurement company. Multiple reasons can explain this increase in size.
Sites have been adding more content in an effort to drum up traffic, such as videos, engaging images, interactive plug-ins (comments and feeds) and other code and script-heavy features. Websites are becoming more and more technically advanced, and other sites have to keep adding features to stay competitive.
To keep up with the rapidly increasing number of users accessing sites on various platforms, developers are offering more versions of websites as well as apps to accommodate all devices, including smartphones, watches, tablets, and other gadgets. All of these versions require additional code, ultimately adding to the weight of a given website.
Then there are the advertisers who want to get the user’s attention by creating dramatic displays for their products that consume even more bandwidth.
Websites also want to know who is visiting their pages, both welcome and unwelcome visitors. New tools that track and analyze visitors have increased in popularity, as well as stronger encryption technology to add more security. These security measures and trackers require more code, again slowing load times.

Unfortunately for websites trying to keep up with the times, Google has just introduced a new ‘Slow to Load’ warning sign in mobile search results. Since mobile searches account for more than half of the total Google searches in 10 countries, Google wants to enhance user experience for those on their mobile platform.
Although the weight of a website isn’t all that contributes to slow loading, it’s a major factor. Other reasons include users overusing data, a poor connection, or a high level of traffic in the mobile network.
Google also changed its algorithm in April, so now ‘mobile friendly’ sites are ranked higher on search results, while those that fail to meet its criteria are ranked lower.
Although the internet is only slowing by a matter of seconds, it’s still slowing down. All the more reason for a user to become frustrated with a page that’s taking a couple extra seconds to load and go to a competitor’s site.
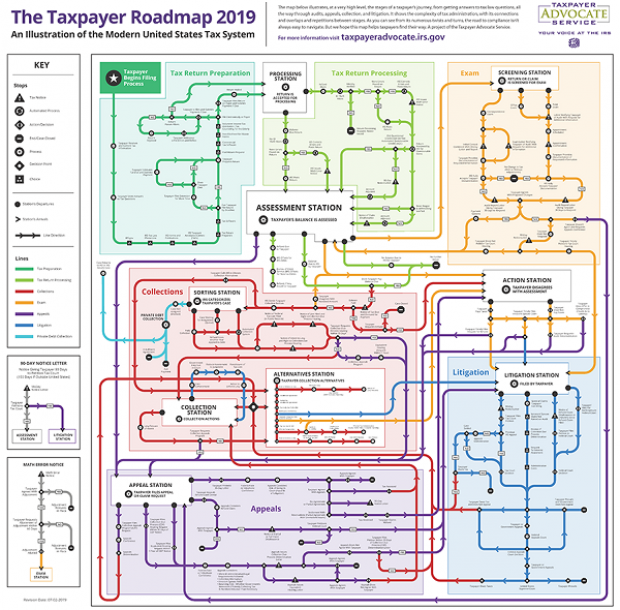
Map of the Day: Navigating the IRS

The Taxpayer Advocate Service – an independent organization within the IRS whose roughly 1,800 employees both assist taxpayers in resolving problems with the tax collection agency and recommend changes aimed at improving the system – released a “subway map” that shows the “the stages of a taxpayer’s journey.” The colorful diagram includes the steps a typical taxpayer takes to prepare and file their tax forms, as well as the many “stations” a tax return can pass through, including processing, audits, appeals and litigation. Not surprisingly, the map is quite complicated. Click here to review a larger version on the taxpayer advocate’s site.
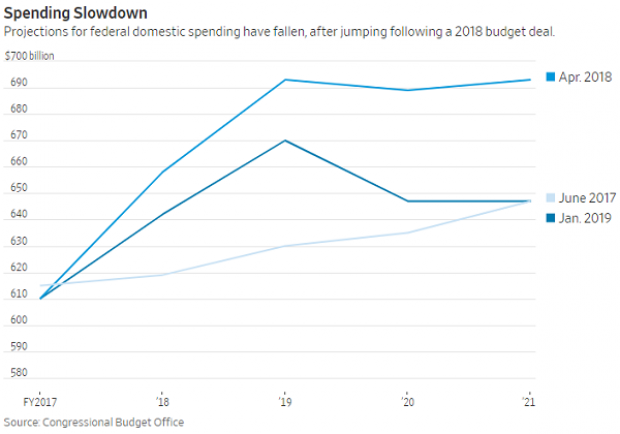
A Surprise Government Spending Slowdown

Economists expected federal spending to boost growth in 2019, but some of the fiscal stimulus provided by the 2018 budget deal has failed to show up this year, according to Kate Davidson of The Wall Street Journal.
Defense spending has come in as expected, but nondefense spending has lagged, and it’s unlikely to catch up to projections even if it accelerates in the coming months. Lower spending on disaster relief, the government shutdown earlier this year, and federal agencies spending less than they have been given by Congress all appear to be playing a role in the spending slowdown, Davidson said.
Number of the Day: $203,500

The Wall Street Journal’s Catherine Lucey reports that acting White House Chief of Staff Mick Mulvaney is making a bit more than his predecessors: “The latest annual report to Congress on White House personnel shows that President Trump’s third chief of staff is getting an annual salary of $203,500, compared with Reince Priebus and John Kelly, each of whom earned $179,700.” The difference is the result of Mulvaney still technically occupying the role of director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, where his salary level is set by law.
The White House told the Journal that if Mulvaney is made permanent chief of staff his salary would be adjusted to the current salary for an assistant to the president, $183,000.
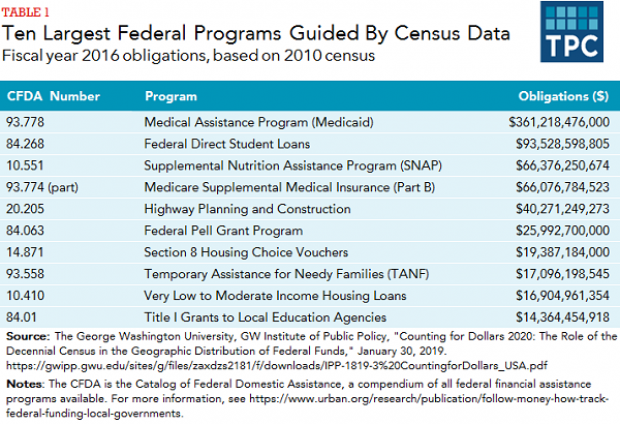
The Census Affects Nearly $1 Trillion in Spending

The 2020 census faces possible delay as the Supreme Court sorts out the legality of a controversial citizenship question added by the Trump administration. Tracy Gordon of the Tax Policy Center notes that in addition to the basic issue of political representation, the decennial population count affects roughly $900 billion in federal spending, ranging from Medicaid assistance funds to Section 8 housing vouchers. Here’s a look at the top 10 programs affected by the census:
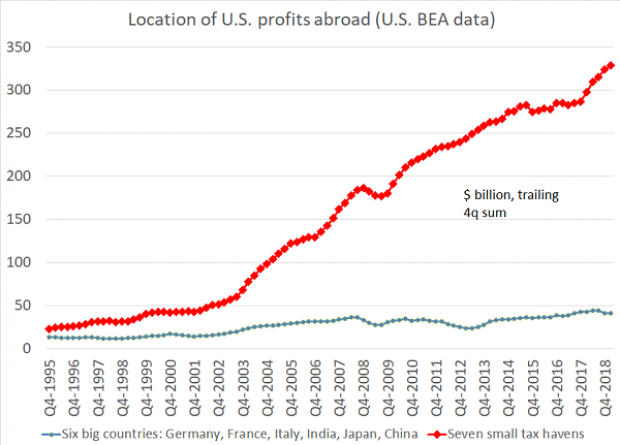
Chart of the Day: Offshore Profits Continue to Rise

Brad Setser, a former U.S. Treasury economist now with the Council on Foreign Relations, added another detail to his assessment of the foreign provisions of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act: “A bit more evidence that Trump's tax reform didn't change incentives to offshore profits: the enormous profits that U.S. firms report in low tax jurisdictions continues to rise,” Setser wrote. “In fact, there was a bit of a jump up over the course of 2018.”