The Washington Post Closes a Window on Hackers and Big Government

The Washington Post is pushing back against government surveillance, hackers and other nosy folks trying to get a peek at you and your data.
Starting Tuesday it will begin to encrypt parts of its website to make it more difficult to track the reading habits of visitors. The encryption will apply to the Post’s homepage, stories on the site’s national security page and The Switch, its technology policy blog.
A display icon of a small lock in the web address bar will signal readers that pages are encrypted. In addition, the secure pages will start with the letters “https,” rather than the standard “http.”
The encryption also has the potential to make it tougher for governments to censor content. If censors are monitoring website traffic, they can see only the domain a person is visiting, not the specific page. A country would have to block the entire website if it wanted to block content.
The Post acknowledges that the additional security measures could make online advertising less attractive to companies. Advertisers might also be driven away by having to make sure their content is also secure, an extra step some companies might not be willing to take.
The Post is the first major news organization to introduce such security measures. Last fall, The New York Times published a blog post imploring websites to implement secure connections, but it has yet to follow through on its own challenge.
However, other smaller news sources, such as the Intercept and TechDirt, use https technology by default.
Encrypted traffic is becoming increasingly common for many sites, including online banking and web-based email services. Earlier this month, the Obama administration ordered all public federal websites to begin using https technology by the end of 2016.
The social media giant Facebook announced in early June that users could encrypt notifications sent from the website to a user’s personal email address, protecting potentially sensitive emails. Facebook – as well as hackers, spies and others -- will be denied access to the user’s private encryption key.
This move prevents hackers who have accessed a user’s email inbox from being able to understand emails from Facebook without knowing their private key. While a user’s activity on the actual site will not be encrypted, this announcement could be the first in a series of moves to protect Facebooks’ user privacy.
Apple and Google have also implemented more security measures for user privacy over the last year.
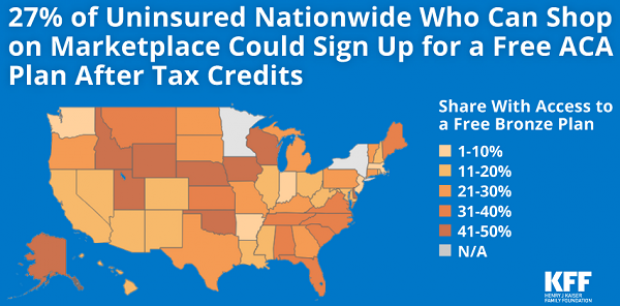
4.2 Million Uninsured People Could Get Free Obamacare Plans

About 4.2 million uninsured people could sign up for a bronze-level Obamacare health plan and pay nothing for it after tax credits are applied, the Kaiser Family Foundation said Tuesday. That means that 27 percent of the country’s 15.9 million uninsured people could get covered for free. The chart below breaks down the eligible population by state.
Takedown of the Day: Ezra Klein on Paul Ryan's Legacy of Debt

Vox’s Ezra Klein says that retiring House Speaker Paul Ryan’s legacy can be summed up in one number: $343 billion. “That’s the increase between the deficit for fiscal year 2015 and fiscal year 2018— that is, the difference between the fiscal year before Ryan became speaker of the House and the fiscal year in which he retired.”
Klein writes that Ryan’s choices while in office — especially the 2017 tax cuts and the $1.3 trillion spending bill he helped pass and the expansion of the earned income tax credit he talked up but never acted on — should be what define his legacy:
“[N]ow, as Ryan prepares to leave Congress, it is clear that his critics were correct and a credulous Washington press corps — including me — that took him at his word was wrong. In the trillions of long-term debt he racked up as speaker, in the anti-poverty proposals he promised but never passed, and in the many lies he told to sell unpopular policies, Ryan proved as much a practitioner of post-truth politics as Donald Trump. …
“Ultimately, Ryan put himself forward as a test of a simple, but important, proposition: Is fiscal responsibility something Republicans believe in or something they simply weaponize against Democrats to win back power so they can pass tax cuts and defense spending? Over the past three years, he provided a clear answer. That is his legacy, and it will haunt his successors.”
Number of the Day: $300 Million

Mick Mulvaney, the acting director of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, wants the agency to be known as the Bureau of Consumer Financial Protection, the name under which it was established by Title X of the 2010 Dodd-Frank Wall Street reform law. Mulvaney even had new signage put up in the lobby of the bureau. But the rebranding could cost the banks and other financial businesses regulated by the bureau more than $300 million, according to an internal agency analysis reported by The Hill’s Sylvan Lane. The costs would arise from having to update internal databases, regulatory filings and disclosure forms with the new name. The rebranding would cost the agency itself between $9 million and $19 million, the analysis estimated. Lane adds that it’s not clear whether Kathy Kraninger, President Trump’s nominee to serve as the bureau’s full-time director, would follow through on Mulvaney’s name change once she is confirmed by the Senate.
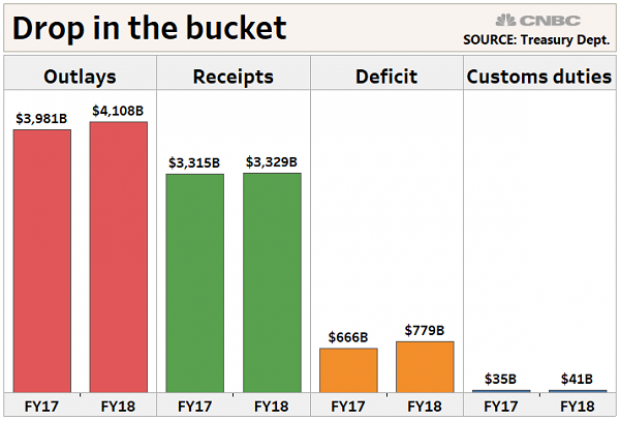
Why Trump's Tariffs Are Just a Drop in the Bucket

President Trump said this week that tariff increases by his administration are producing "billions of dollars" in revenues, thereby improving the country’s fiscal situation. But CNBC’s John Schoen points out that while tariff revenues are indeed higher by several billion dollars this year, the total revenue is a drop in the bucket compared to the sheer size of government outlays and receipts – and the growing annual deficit.
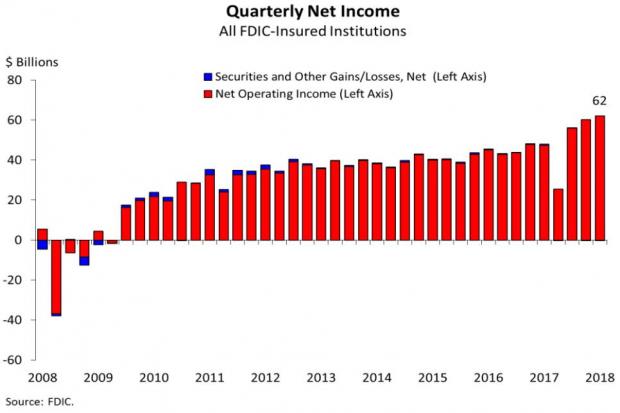
Bank Profits Hit New Record Thanks to 2017 Tax Law

Bank profits reached a record $62 billion in the third quarter, up $14 billion, or 29.3 percent, from the same period last year, according to data from the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. The FDIC said that about half of the increase in net income was attributable to last year’s tax cuts. The FDIC estimated that, with the effective tax rates from before the new law, bank profits for the quarter would have risen by about 14 percent, to $54.6 billion.