The Washington Post Closes a Window on Hackers and Big Government

The Washington Post is pushing back against government surveillance, hackers and other nosy folks trying to get a peek at you and your data.
Starting Tuesday it will begin to encrypt parts of its website to make it more difficult to track the reading habits of visitors. The encryption will apply to the Post’s homepage, stories on the site’s national security page and The Switch, its technology policy blog.
A display icon of a small lock in the web address bar will signal readers that pages are encrypted. In addition, the secure pages will start with the letters “https,” rather than the standard “http.”
The encryption also has the potential to make it tougher for governments to censor content. If censors are monitoring website traffic, they can see only the domain a person is visiting, not the specific page. A country would have to block the entire website if it wanted to block content.
The Post acknowledges that the additional security measures could make online advertising less attractive to companies. Advertisers might also be driven away by having to make sure their content is also secure, an extra step some companies might not be willing to take.
The Post is the first major news organization to introduce such security measures. Last fall, The New York Times published a blog post imploring websites to implement secure connections, but it has yet to follow through on its own challenge.
However, other smaller news sources, such as the Intercept and TechDirt, use https technology by default.
Encrypted traffic is becoming increasingly common for many sites, including online banking and web-based email services. Earlier this month, the Obama administration ordered all public federal websites to begin using https technology by the end of 2016.
The social media giant Facebook announced in early June that users could encrypt notifications sent from the website to a user’s personal email address, protecting potentially sensitive emails. Facebook – as well as hackers, spies and others -- will be denied access to the user’s private encryption key.
This move prevents hackers who have accessed a user’s email inbox from being able to understand emails from Facebook without knowing their private key. While a user’s activity on the actual site will not be encrypted, this announcement could be the first in a series of moves to protect Facebooks’ user privacy.
Apple and Google have also implemented more security measures for user privacy over the last year.
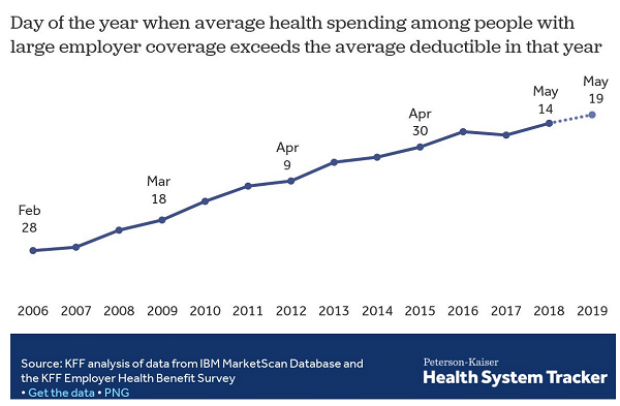
Coming Soon: Deductible Relief Day!

You may be familiar with the concept of Tax Freedom Day – the date on which you have earned enough to pay all of your taxes for the year. Focusing on a different kind of financial burden, analysts at the Kaiser Family Foundation have created Deductible Relief Day – the date on which people in employer-sponsored insurance plans have spent enough on health care to meet the average annual deductible.
Average deductibles have more than tripled over the last decade, forcing people to spend more out of pocket each year. As a result, Deductible Relief Day is “getting later and later in the year,” Kaiser’s Larry Levitt said in a tweet Thursday.
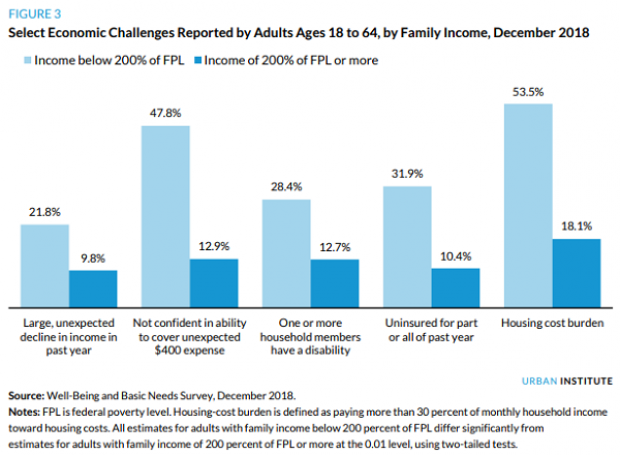
Chart of the Day: Families Still Struggling

Ten years into what will soon be the longest economic expansion in U.S. history, 40% of families say they are still struggling, according to a new report from the Urban Institute. “Nearly 4 in 10 nonelderly adults reported that in 2018, their families experienced material hardship—defined as trouble paying or being unable to pay for housing, utilities, food, or medical care at some point during the year—which was not significantly different from the share reporting these difficulties for the previous year,” the report says. “Among adults in families with incomes below twice the federal poverty level (FPL), over 60 percent reported at least one type of material hardship in 2018.”
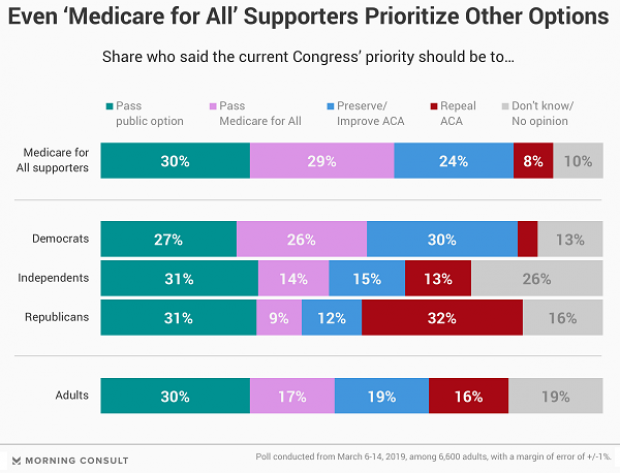
Chart of the Day: Pragmatism on a Public Option

A recent Morning Consult poll 3,073 U.S. adults who say they support Medicare for All shows that they are just as likely to back a public option that would allow Americans to buy into Medicare or Medicaid without eliminating private health insurance. “The data suggests that, in spite of the fervor for expanding health coverage, a majority of Medicare for All supporters, like all Americans, are leaning into their pragmatism in response to the current political climate — one which has left many skeptical that Capitol Hill can jolt into action on an ambitious proposal like Medicare for All quickly enough to wrangle the soaring costs of health care,” Morning Consult said.
Chart of the Day: The Explosive Growth of the EITC

The Earned Income Tax Credit, a refundable tax credit for low- to moderate-income workers, was established in 1975, with nominal claims of about $1.2 billion ($5.6 billion in 2016 dollars) in its first year. According to the Tax Policy Center, by 2016 “the total was $66.7 billion, almost 12 times larger in real terms.”
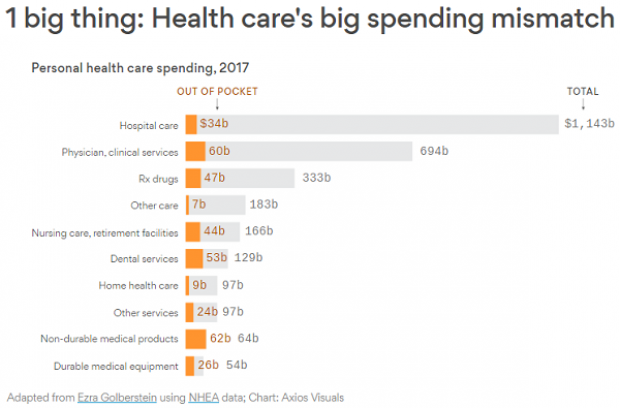
Chart of the Day: The Big Picture on Health Care Costs

“The health care services that rack up the highest out-of-pocket costs for patients aren't the same ones that cost the most to the health care system overall,” says Axios’s Caitlin Owens. That may distort our view of how the system works and how best to fix it. For example, Americans spend more out-of-pocket on dental services ($53 billion) than they do on hospital care ($34 billion), but the latter is a much larger part of national health care spending as a whole.