Feeling Flush, More Parents Open Their Wallets for College Spending

As lingering financial fears from the recession fade, more parents are willing and able to open their wallets to pay for their children’s educations.
Parents have become the top source of college funding for the first time since 2010. According to a new report from private student loan lender Sallie Mae’s, parental income and savings covered 32 percent of college costs in the academic year 2014-15, while scholarships and grants covered 30 percent.
Families spent an average of $24,164 on college this year, a 16 percent rise in spending from the previous year and the largest increase since 2009-10. The money spent covers costs of tuition, books, and living expenses.
Related: Average Family Has Saved Enough to Send One Kid to College for Half a Year
The report details how fewer parents fear the worst when it comes to the risks associated with college. Fewer parents are worried that their child won’t find a job after graduation, that their income will decline because of layoffs, and that there will be an increase in student loan rates. As confidence has increased, fewer families are using cost-saving techniques, such as having students live at home.
Another factor contributing to the willingness of parents to spend on education is the improving stock market. The average size of a 529 account, the popular college savings investment plan, continues to grow after the recession caused a downturn, hitting a balance of $20,474 as of December 1, 2014. That figure tumbled to $10,690 at the end of 2008, according to data from the College Savings Plan Network.
Although parents may be feeling better about paying for college, the basic trend of increasing prices continues, and loans are still a big part of the funding picture. Between 2001 and 2012, average undergraduate tuition almost doubled, causing an average real rate increase of 3.5 percent each year. Nearly 71 percent of college graduates left school with student loan debt this year, up from 54 percent 20 years prior. The average debt was $35,000 in 2015, an increase of 34 percent from 2010, student loan-tracker Edvisors has found.
Stat of the Day: 0.2%

The New York Times’ Jim Tankersley tweets: “In order to raise enough revenue to start paying down the debt, Trump would need tariffs to be ~4% of GDP. They're currently 0.2%.”
Read Tankersley’s full breakdown of why tariffs won’t come close to eliminating the deficit or paying down the national debt here.
Number of the Day: 44%

The “short-term” health plans the Trump administration is promoting as low-cost alternatives to Obamacare aren’t bound by the Affordable Care Act’s requirement to spend a substantial majority of their premium revenues on medical care. UnitedHealth is the largest seller of short-term plans, according to Axios, which provided this interesting detail on just how profitable this type of insurance can be: “United’s short-term plans paid out 44% of their premium revenues last year for medical care. ACA plans have to pay out at least 80%.”
Number of the Day: 4,229

The Washington Post’s Fact Checkers on Wednesday updated their database of false and misleading claims made by President Trump: “As of day 558, he’s made 4,229 Trumpian claims — an increase of 978 in just two months.”
The tally, which works out to an average of almost 7.6 false or misleading claims a day, includes 432 problematics statements on trade and 336 claims on taxes. “Eighty-eight times, he has made the false assertion that he passed the biggest tax cut in U.S. history,” the Post says.
Number of the Day: $3 Billion

A new analysis by the Department of Health and Human Services finds that Medicare’s prescription drug program could have saved almost $3 billion in 2016 if pharmacies dispensed generic drugs instead of their brand-name counterparts, Axios reports. “But the savings total is inflated a bit, which HHS admits, because it doesn’t include rebates that brand-name drug makers give to [pharmacy benefit managers] and health plans — and PBMs are known to play games with generic drugs to juice their profits.”
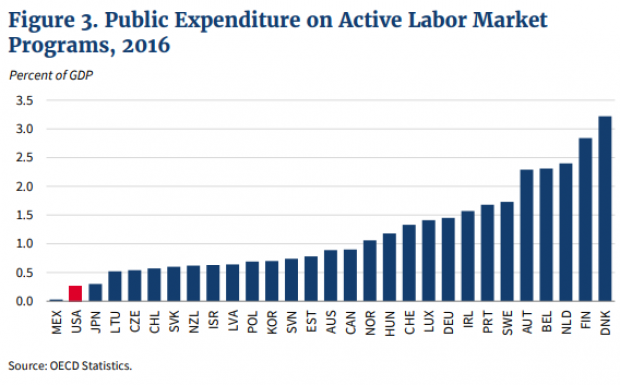
Chart of the Day: Public Spending on Job Programs

President Trump announced on Thursday the creation of a National Council for the American Worker, charged with developing “a national strategy for training and retraining workers for high-demand industries,” his daughter Ivanka wrote in The Wall Street Journal. A report from the president’s National Council on Economic Advisers earlier this week made it clear that the U.S. currently spends less public money on job programs than many other developed countries.