5 Cities with the Most Credit Card Debt
Why is the Lone Star State racking up so much debt? Its two largest cities—Dallas and Houston/Fort Worth make the list of the cities with the most credit card debt, and San Antonio comes in as No. 1.
The new study from CreditCards.com used credit report data from Experian to compare the average credit card debt in the 25 largest U.S. metro areas with each area’s median income. It assumed that 15 percent of a person's monthly income would be spent on paying down credit card debt.
The analysis claims it would take San Antonio residents with median incomes of $27,491 a full 16 months to pay off an average of $4,880, making monthly payments of $344 a month. By comparison, a resident of San Francisco making $42,613 a year would pay off $4,393 in credit card debt with nine monthly payments of $533 per month.
The cities with the highest credit card debt burdens were:
- San Antonio
- Dallas/Fort Worth
- Atlanta
- Miami/Fort Lauderdale
- Houston
Related: 5 Reasons to Pay Off Your Credit Card Debt Now
The metro areas with the highest debt don’t necessarily have the highest debt burdens when adjusted for income. For example, Washington, D.C. has the nation’s highest average credit card debt at $5,046, but since it also has the highest median income in the nation, its debt burden is lower. By applying 15 percent of their paychecks, residents can pay off that debt in 10 months.
The cities with the lowest credit card debt burdens were:
- New York City
- Minneapolis/St. Paul
- Washington, D.C.
- Boston
- San Francisco/Oakland/San Jose
Matt Schulz, senior industry analyst at CreditCards.com, points out that there isn’t much difference between the city with the highest credit card debt, Washington, D.C. ($5,046), and the city with the lowest credit card debt, the Riverside-San Bernardino area ($4,137), but there is a big difference in income. A higher income means that debts can be paid off more quickly. “It really is all about earnings,” Schulz says. “People are using their credit cards whether they live in the biggest city in the country or they live in the 25th biggest city in the country.”
While most folks won’t be able to increase their income that dramatically, there are still steps they can take to make sure they’re tackling their credit card debt in the most effective way possible.
Related: How to Defuse Exploding Consumer Credit Debt
His advice to consumers? “Absolutely, positively pay more than the minimum on your credit card balance every month.” And the next best thing? “If you can’t pay the full balance, then you have to pay off more than the minimum.”
Schulz also recommends calling the credit card issuer and asking if you can get better terms. “It’s certainly worth a call,” says Schulz. “We did a study last year that showed that 65 percent of people who asked for a lower interest rate got a lower APR.” The same study said that 86 percent of people who asked for a waiver of a late payment fee were successful in getting the charge removed.
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- The Next Debt Crisis Could Be Much Worse than in 2013, GAO Warns
- The New Generation of ‘Genuinely Creepy’ Electronic Devices
- 9 Social Security Tips You Need to Know Right Now
Wages Are Finally Going Up, Sort of

Average hourly earnings last month rose by 2.9 percent from a year earlier, the Labor Department said Friday — the fastest wage growth since the recession ended in 2009. The economy added 201,000 jobs in August, marking the 95th straight month of gains, while the unemployment rate held steady at 3.9 percent.
Analysts noted, though, that the welcome wage gains merely kept pace with a leading measure of inflation, meaning that pay increases are largely or entirely being canceled out by higher prices. “The last time unemployment was this low, during the dot-com boom, wage growth was significantly faster — well above 3.5 percent,” The Washington Post’s Heather Long wrote. The White House Council of Economic Advisers this week issued a report arguing that wage gains over the past year have been better than they appear in official statistics.
Cost of Trump’s Military Parade Rising Fast

It looks like President Trump’s military parade is going to cost a lot more than the initial estimate suggested – about $80 million more.
The Department of Defense pegged the cost of the parade at roughly $12 million back in July, but CNBC reported Thursday that Pentagon officials have increased their estimate to $92 million. The total consists of $50 million from the Defense Department and $42 million from other agencies, including the Department of Homeland Security.
The parade, which President Trump requested after attending a Bastille Day military parade in Paris last year, is scheduled for November 10 and will reportedly include aircraft, armored vehicles and soldiers in period uniforms. Abrams tanks, which weigh roughly 70 tons apiece, will also be included, CNBC said, despite concerns about heavy military equipment ripping up the streets of Washington. A Pentagon analysis apparently found that the armored vehicle’s treads would not cause any damage.
The parade is expected to begin at the Capitol, continue past the White House and end at the National Mall, according to earlier reports from NBC News.
Quote of the Day: Time to Raise Taxes?

“Tax revenue as a percentage of gross domestic product is expected to be 16.5 percent next year. The long-term average in a full-employment economy is 18.5 percent of GDP; if revenue were at that level for the coming decade, debt would be $3.2 trillion lower and the 10-year fiscal gap would be halved. Returning to past revenue levels, however, will be inadequate over time, because an aging population will increase Medicare and Social Security costs. This need not pose a problem: Revenue was roughly 19 percent of GDP in the late 1990s, and economic conditions were excellent.”
– Former U.S. Treasury Secretary Richard E. Rubin, writing in The Washington Post
Quote of the Day: When Tax Cuts Pay for Themselves

“You … often hear the claim that a lot of tax cuts will ‘pay for themselves,’ that they’ll cause so much additional economic activity that the revenue feedback from that activity will fully offset the direct revenue loss caused by the tax cut so that you end up making money for the federal government, or at least not losing any money. Now, of course that is theoretically possible and it would happen at extreme rates. I mean if a country had a 99 percent flat rate income tax and lowered it to 98 percent, I believe that they almost certainly would collect more revenue at the 98 percent rate than they did at the 99 percent rate. But the idea that this type of effect would occur at today’s tax levels just requires responses that are much bigger than statistical evidence would support and I think much bigger than common sense would indicate if you just ask people how they themselves would react to the tax cut.”
-- Alan Viard, tax policy expert at the American Enterprise Institute
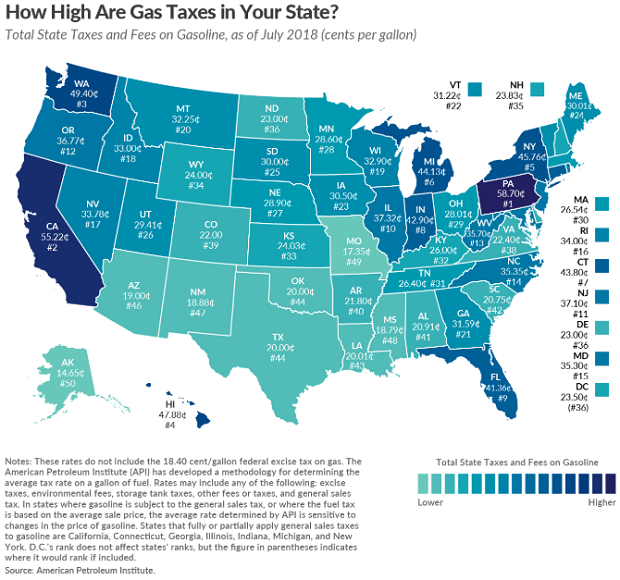
Map of the Day: Gas Taxes

It’s summertime and the driving is anything but easy if you want to get to your favorite beach or mountain cabin for a well-deserved break. As lawmakers consider a plan to raise federal fuel taxes by 15 cents a gallon, here’s a look at the current state-level taxes on gasoline, courtesy of the Tax Foundation: