The Best and Worst States for Student Debt

Where you go to college and what major you pick can have huge financial consequences, but where you live after graduating can also have a big impact on how much your diploma is worth — and how well you can handle your student debt.
How likely are you to land a good paying job? How high will your living expenses be? The answers to those questions and others like them go a long way to determining how burdensome those monthly student loans payments are.
Related: The Best Investment the U.S. Could Make—Affordable Higher Education
To ensure your loan doesn’t break you, experts suggest that your payment should not exceed 8 to 10 percent of your monthly income.
Unsurprisingly, the personal finance website WalletHub says, “Student-loan borrowers will fare better in states that produce a combination of lower college-related debt levels, stronger economies and higher incomes.”
To find those states, WalletHub looked at seven metrics, with special emphasis given to student debt as a percentage of average income, the local unemployment rate for people aged 25 to 34 and the percentage of borrowers aged 50 or older. Here are the 10 best and worst states for student debt. You can click on your state on the map below to see where it ranks.
Related: Private Student Loans: Everything You Need to Know
10 Best States for Student Debt
- Utah
- Wyoming
- North Dakota
- Washington
- Nebraska
- Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Minnesota
- Colorado
- South Dakota
10 Worst States for Student Debt
- Mississippi
- Rhode Island
- Connecticut
- Maine
- Georgia
- South Carolina
- New York
- Alabama
- West Virginia
- Oregon
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
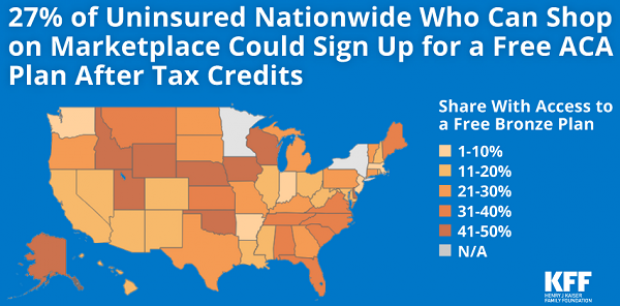
4.2 Million Uninsured People Could Get Free Obamacare Plans

About 4.2 million uninsured people could sign up for a bronze-level Obamacare health plan and pay nothing for it after tax credits are applied, the Kaiser Family Foundation said Tuesday. That means that 27 percent of the country’s 15.9 million uninsured people could get covered for free. The chart below breaks down the eligible population by state.
Takedown of the Day: Ezra Klein on Paul Ryan's Legacy of Debt

Vox’s Ezra Klein says that retiring House Speaker Paul Ryan’s legacy can be summed up in one number: $343 billion. “That’s the increase between the deficit for fiscal year 2015 and fiscal year 2018— that is, the difference between the fiscal year before Ryan became speaker of the House and the fiscal year in which he retired.”
Klein writes that Ryan’s choices while in office — especially the 2017 tax cuts and the $1.3 trillion spending bill he helped pass and the expansion of the earned income tax credit he talked up but never acted on — should be what define his legacy:
“[N]ow, as Ryan prepares to leave Congress, it is clear that his critics were correct and a credulous Washington press corps — including me — that took him at his word was wrong. In the trillions of long-term debt he racked up as speaker, in the anti-poverty proposals he promised but never passed, and in the many lies he told to sell unpopular policies, Ryan proved as much a practitioner of post-truth politics as Donald Trump. …
“Ultimately, Ryan put himself forward as a test of a simple, but important, proposition: Is fiscal responsibility something Republicans believe in or something they simply weaponize against Democrats to win back power so they can pass tax cuts and defense spending? Over the past three years, he provided a clear answer. That is his legacy, and it will haunt his successors.”
Number of the Day: $300 Million

Mick Mulvaney, the acting director of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, wants the agency to be known as the Bureau of Consumer Financial Protection, the name under which it was established by Title X of the 2010 Dodd-Frank Wall Street reform law. Mulvaney even had new signage put up in the lobby of the bureau. But the rebranding could cost the banks and other financial businesses regulated by the bureau more than $300 million, according to an internal agency analysis reported by The Hill’s Sylvan Lane. The costs would arise from having to update internal databases, regulatory filings and disclosure forms with the new name. The rebranding would cost the agency itself between $9 million and $19 million, the analysis estimated. Lane adds that it’s not clear whether Kathy Kraninger, President Trump’s nominee to serve as the bureau’s full-time director, would follow through on Mulvaney’s name change once she is confirmed by the Senate.
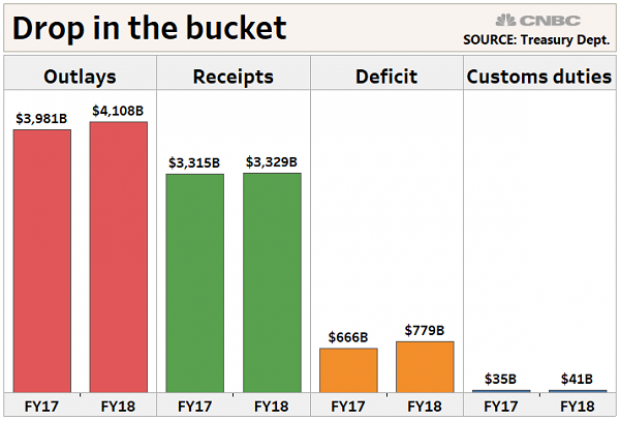
Why Trump's Tariffs Are Just a Drop in the Bucket

President Trump said this week that tariff increases by his administration are producing "billions of dollars" in revenues, thereby improving the country’s fiscal situation. But CNBC’s John Schoen points out that while tariff revenues are indeed higher by several billion dollars this year, the total revenue is a drop in the bucket compared to the sheer size of government outlays and receipts – and the growing annual deficit.
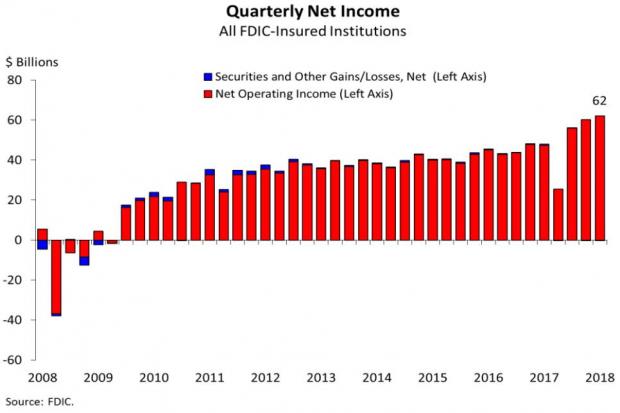
Bank Profits Hit New Record Thanks to 2017 Tax Law

Bank profits reached a record $62 billion in the third quarter, up $14 billion, or 29.3 percent, from the same period last year, according to data from the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. The FDIC said that about half of the increase in net income was attributable to last year’s tax cuts. The FDIC estimated that, with the effective tax rates from before the new law, bank profits for the quarter would have risen by about 14 percent, to $54.6 billion.