Blame China for Your Costly Lobster Roll

Looking for authentic, down-home Maine lobster? Head to China.
The upsurge in demand for lobster in China this year has caused the price of the succulent marine crustacean to shoot up to record highs in the U.S., according to Bloomberg News. Wholesale prices for lobsters have clawed 32 percent higher over the last year.
Lacking a lobster industry itself, China used to rely on Australian imports to meet the demand from an expanding middle class that views lobster as a status symbol. But in 2012, as catches off of Western Australia began dwindling and prices of lobster fell in the Gulf of Maine, China changed its main supplier to the U.S.
Related: McDonald’s Aims for a Classier Crowd with Lobster Rolls
Lobster exports from the East Coast are the main reason for the hike in fish and seafood exports to China in recent years, according to U.S. Department of Agriculture data. Over the past seven months, about 60,000 live North American lobsters a week make the 7,500-mile trek halfway across the world. The lobsters must still be alive by the time they arrive in China or else they lack appeal, so they’re packed in wet newspapers and Styrofoam coolers for a trip that must be made in 18 hours or less, according to Bloomberg.
Another reason for the surge in prices was the bitterly cold winter this year, which slowed the catch in Canada and delayed the summer harvest in Maine.
Holding off on your lobster roll until next summer in the hopes that prices will wane? Don’t count on it. The Chinese middle class is still growing rapidly, and the country already consumes 35 percent of the world’s seafood — a number likely to increase.
Top Reads from The Fiscal Times:
- Born in the USA: 24 Iconic American Foods
- America’s 10 Top Selling Medications
- You’re Richer Than You Think. Really.
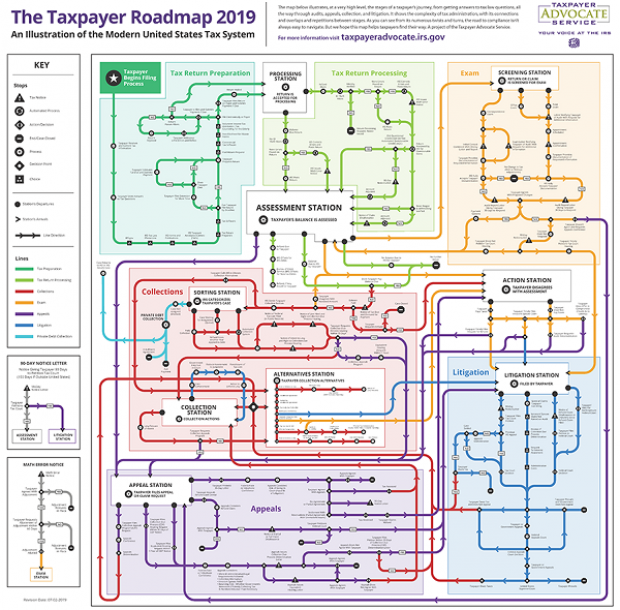
Map of the Day: Navigating the IRS

The Taxpayer Advocate Service – an independent organization within the IRS whose roughly 1,800 employees both assist taxpayers in resolving problems with the tax collection agency and recommend changes aimed at improving the system – released a “subway map” that shows the “the stages of a taxpayer’s journey.” The colorful diagram includes the steps a typical taxpayer takes to prepare and file their tax forms, as well as the many “stations” a tax return can pass through, including processing, audits, appeals and litigation. Not surprisingly, the map is quite complicated. Click here to review a larger version on the taxpayer advocate’s site.
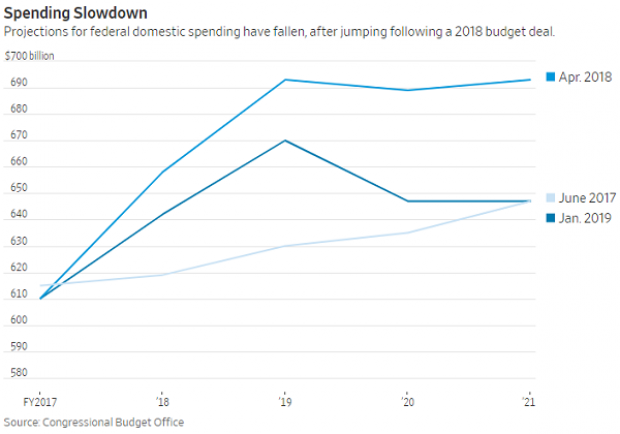
A Surprise Government Spending Slowdown

Economists expected federal spending to boost growth in 2019, but some of the fiscal stimulus provided by the 2018 budget deal has failed to show up this year, according to Kate Davidson of The Wall Street Journal.
Defense spending has come in as expected, but nondefense spending has lagged, and it’s unlikely to catch up to projections even if it accelerates in the coming months. Lower spending on disaster relief, the government shutdown earlier this year, and federal agencies spending less than they have been given by Congress all appear to be playing a role in the spending slowdown, Davidson said.
Number of the Day: $203,500

The Wall Street Journal’s Catherine Lucey reports that acting White House Chief of Staff Mick Mulvaney is making a bit more than his predecessors: “The latest annual report to Congress on White House personnel shows that President Trump’s third chief of staff is getting an annual salary of $203,500, compared with Reince Priebus and John Kelly, each of whom earned $179,700.” The difference is the result of Mulvaney still technically occupying the role of director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, where his salary level is set by law.
The White House told the Journal that if Mulvaney is made permanent chief of staff his salary would be adjusted to the current salary for an assistant to the president, $183,000.
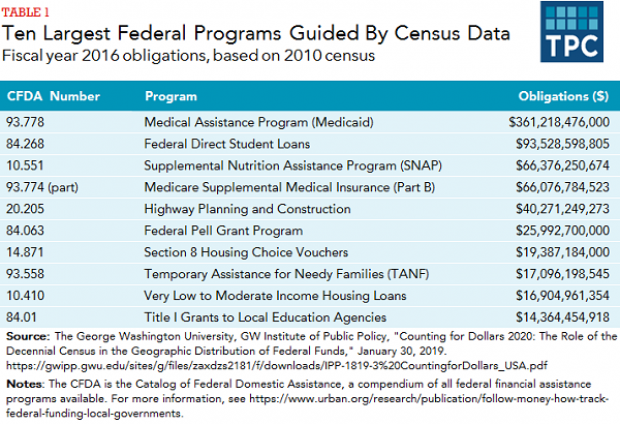
The Census Affects Nearly $1 Trillion in Spending

The 2020 census faces possible delay as the Supreme Court sorts out the legality of a controversial citizenship question added by the Trump administration. Tracy Gordon of the Tax Policy Center notes that in addition to the basic issue of political representation, the decennial population count affects roughly $900 billion in federal spending, ranging from Medicaid assistance funds to Section 8 housing vouchers. Here’s a look at the top 10 programs affected by the census:
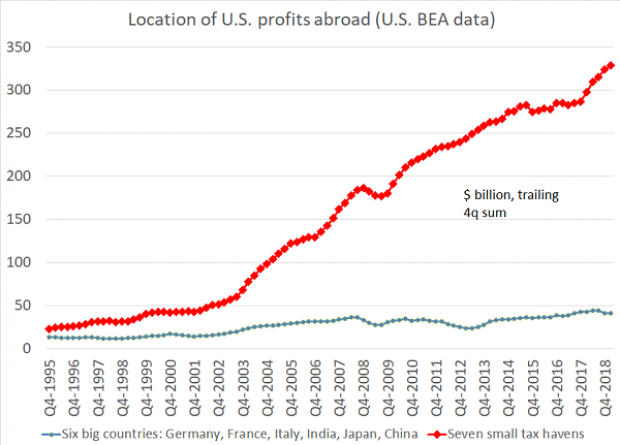
Chart of the Day: Offshore Profits Continue to Rise

Brad Setser, a former U.S. Treasury economist now with the Council on Foreign Relations, added another detail to his assessment of the foreign provisions of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act: “A bit more evidence that Trump's tax reform didn't change incentives to offshore profits: the enormous profits that U.S. firms report in low tax jurisdictions continues to rise,” Setser wrote. “In fact, there was a bit of a jump up over the course of 2018.”