4 Ways to Fix Social Security

Social Security celebrates its 80th birthday today, and the popular program that provides paychecks for 44 million elderly Americans is in need of a safety net of its own.
As the amount claimed by recipients continues to outpace the amount of money contributed by workers, the system will need to dip into its reserves to keep up with its obligations by 2020. Within 15 years after that (if nothing changes), those reserves will be gone and the system will only be able to pay 77 cents on every dollar owed, an amount that will continue to decrease with time.
The problem is even more acute given that future retirees won’t have the same access to pensions that many current retirees use to fund their retirement, and younger workers haven’t saved nearly enough to cover the costs they’ll face when they stop working.
To close the projected gap, the country needs to raise revenue, reduce benefits or some combination of the two. Here are four of the most commonly proposed solutions:
1. Raise the retirement age. For most Americans, the full retirement age (at which you can get full benefits) ranges from 65 through 67. Advocates of this solution would reduce the amount the government pays in Social Security by gradually pushing back the age at which you’re eligible for full benefits.
The drawback: Many Americans are already forced into retirement before they reach age 65. If they claim early and receive reduced benefits they may not have enough money to meet their basic needs. Also, workers in physically demanding jobs many not be able to work those extra years.
2. Raise the payroll cap. Social Security is funded via payroll taxes, which currently are only levied on the first $118,500 of income. That means that high earners effectively pay a much lower rate toward Social Security than others. Hiking or eliminating that cap, advocates say, would create a fairer system and increase revenue.
The drawback: Critics of this solution claim that increasing taxes on middle- and upper-income earners would reduce their income and stifle the country’s economic growth.
Related: 6 Popular Social Security Myths Busted
3. Institute a means test. While the vast majority of recipients (80 percent, per AARP) rely on Social Security as an integral part of funding their retirement, extremely high net worth individuals don’t need the additional income. This solution would create a net worth or retirement income threshold over which eligibility for social security phases out.
The drawbacks: It could be politically difficult to settle on a threshold, which might vary depending on the geography of a recipient. Plus, this would require people to pay into a system from which they get no benefits.
4. Freeze the cost of living adjustment. Social Security payments have historically been adjusted based on inflation as measured by the Consumer Price Index. This has been minimal in recent years, but the long-term, compounding effect of inflation makes this provision incredibly expensive.The drawbacks: For many people, Social Security is the only inflation-linked retirement income stream that they have. Limiting it could push some retirees over the financial edge as prices rise.
Tax Refunds Rebound

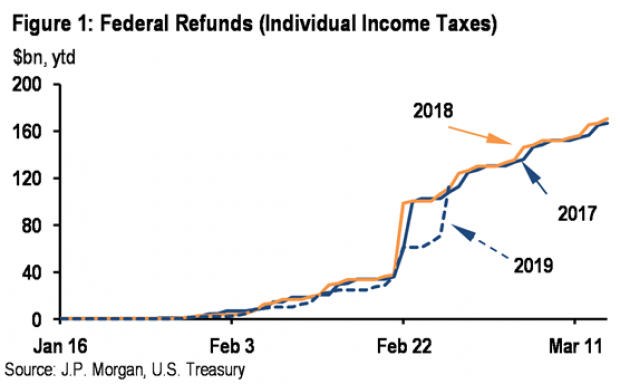
Smaller refunds in the first few weeks of the current tax season were shaping up to be a political problem for Republicans, but new data from the IRS shows that the value of refund checks has snapped back and is now running 1.3 percent higher than last year. The average refund through February 23 last year was $3,103, while the average refund through February 22 of 2019 was $3,143 – a difference of $40. The chart below from J.P. Morgan shows how refunds performed over the last 3 years.
Number of the Day: $22 Trillion

The total national debt surpassed $22 trillion on Monday. Total public debt outstanding reached $22,012,840,891,685.32, to be exact. That figure is up by more than $1.3 trillion over the past 12 months and by more than $2 trillion since President Trump took office.
Chart of the Week: The Soaring Cost of Insulin
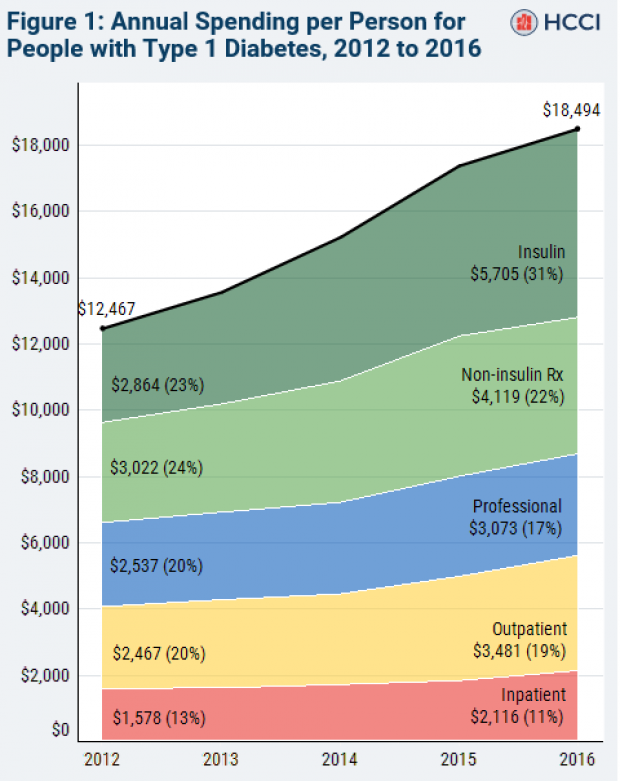
The cost of insulin used to treat Type 1 diabetes nearly doubled between 2012 and 2016, according to an analysis released this week by the Health Care Cost Institute. Researchers found that the average point-of-sale price increased “from $7.80 a day in 2012 to $15 a day in 2016 for someone using an average amount of insulin (60 units per day).” Annual spending per person on insulin rose from $2,864 to $5,705 over the five-year period. And by 2016, insulin costs accounted for nearly a third of all heath care spending for those with Type 1 diabetes (see the chart below), which rose from $12,467 in 2012 to $18,494.
Chart of the Day: Shutdown Hits Like a Hurricane

The partial government shutdown has hit the economy like a hurricane – and not just metaphorically. Analysts at the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget said Tuesday that the shutdown has now cost the economy about $26 billion, close to the average cost of $27 billion per hurricane calculated by the Congressional Budget Office for storms striking the U.S. between 2000 and 2015. From an economic point of view, it’s basically “a self-imposed natural disaster,” CRFB said.
Chart of the Week: Lowering Medicare Drug Prices
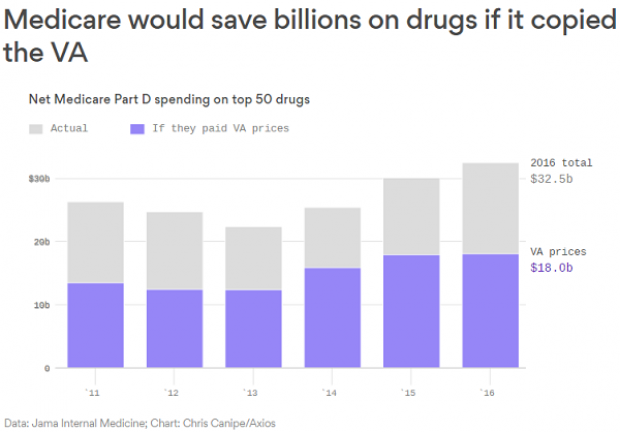
The U.S. could save billions of dollars a year if Medicare were empowered to negotiate drug prices directly with pharmaceutical companies, according to a paper published by JAMA Internal Medicine earlier this week. Researchers compared the prices of the top 50 oral drugs in Medicare Part D to the prices for the same drugs at the Department of Veterans Affairs, which negotiates its own prices and uses a national formulary. They found that Medicare’s total spending was much higher than it would have been with VA pricing.
In 2016, for example, Medicare Part D spent $32.5 billion on the top 50 drugs but would have spent $18 billion if VA prices were in effect – or roughly 45 percent less. And the savings would likely be larger still, Axios’s Bob Herman said, since the study did not consider high-cost injectable drugs such as insulin.