You Won’t Believe How Much Diabetes is Costing the U.S.
The budget-busting price of Sovaldi, a drug used to treat hepatitis C has generated wave after wave of media attention, but it’s far from the only drug creating cost problems for patients and insurers.
As Michelle Andrews of Kaiser Health News points out, diabetes affects 29 million Americans, or 10 times as many people as hepatitis C, and the costs of treating it have been rising quickly. And because it’s a chronic condition, people require lifetime care.
Related: Diabetes Detection Up in Pro-Obamacare States
In 2011, the average annual health spending for individuals with diabetes was $14,093. Two years later, it had risen to $14,999, according to the Healthcare Cost Institute. In contrast, a person without diabetes spent about $10,000 less in medical costs in 2013. Pharmacy provider Express Scripts said earlier this year that 2014 marked the fourth year in a row that medication used to treat diabetes were the most expensive of any traditional drug class.
In all, diabetes costs totaled an estimated $245 billion in 2012, including both direct medical expenses and indirect costs from disability and lost work productivity.
While some of the most popular diabetes drugs aren’t particularly expensive, the new brand-name drugs that are continually being introduced offer more effective treatment and fewer side effects — but also come with a higher price tag. Less than half of the diabetes prescription treatments filled in 2014 were generic.
Nearly a century after its discovery in 1921, insulin is still a common form of treatment for the millions of people with type 1 diabetes, yet there is still no generic form available. Patent protection has been extended in some cases due to improvements in existing formulations. Once those patents expire, Andrews notes, biologically similar drugs could replace them and reduce the price by up to 40 percent.
Related: This Disease Hikes Health Care Costs By More than $10,000 a Year
The financial ramifications of diabetes don’t just stem from the cost of drugs or medical treatment — it’s also been proven that people with diabetes have a high-school dropout rate that is six percentage points higher than those without the disease, according to a Health Affairs study. In addition, young adults with diabetes are four to six percentage points less likely to attend college than those without the disease.
Diabetes also contributes to lower employment and wages. On average, a person with diabetes earns $160,000 less over the course of their lives than people who don’t develop the disease. By age 30, a person with diabetes is 10 percent less likely to be employed.
So even if it’s not generating as many headlines as hepatitis C at any given point in time, the costs of diabetes can’t be ignored.
Top Reads From The Fiscal Times
- The 10 Worst States for Property Taxes
- Two-Thirds of Americans Believe Social Security Is in a Crisis State
- Why McDonald’s Could Suddenly Be Responsible for Millions of New Employees
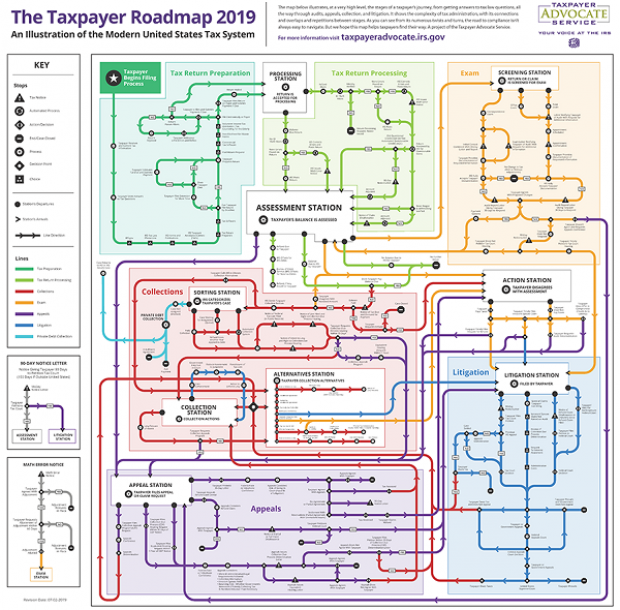
Map of the Day: Navigating the IRS

The Taxpayer Advocate Service – an independent organization within the IRS whose roughly 1,800 employees both assist taxpayers in resolving problems with the tax collection agency and recommend changes aimed at improving the system – released a “subway map” that shows the “the stages of a taxpayer’s journey.” The colorful diagram includes the steps a typical taxpayer takes to prepare and file their tax forms, as well as the many “stations” a tax return can pass through, including processing, audits, appeals and litigation. Not surprisingly, the map is quite complicated. Click here to review a larger version on the taxpayer advocate’s site.
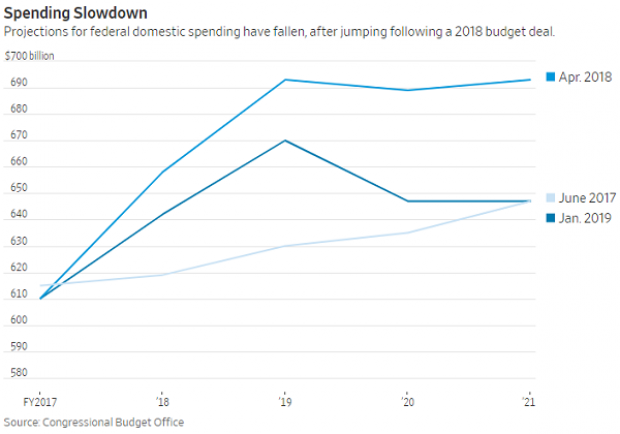
A Surprise Government Spending Slowdown

Economists expected federal spending to boost growth in 2019, but some of the fiscal stimulus provided by the 2018 budget deal has failed to show up this year, according to Kate Davidson of The Wall Street Journal.
Defense spending has come in as expected, but nondefense spending has lagged, and it’s unlikely to catch up to projections even if it accelerates in the coming months. Lower spending on disaster relief, the government shutdown earlier this year, and federal agencies spending less than they have been given by Congress all appear to be playing a role in the spending slowdown, Davidson said.
Number of the Day: $203,500

The Wall Street Journal’s Catherine Lucey reports that acting White House Chief of Staff Mick Mulvaney is making a bit more than his predecessors: “The latest annual report to Congress on White House personnel shows that President Trump’s third chief of staff is getting an annual salary of $203,500, compared with Reince Priebus and John Kelly, each of whom earned $179,700.” The difference is the result of Mulvaney still technically occupying the role of director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, where his salary level is set by law.
The White House told the Journal that if Mulvaney is made permanent chief of staff his salary would be adjusted to the current salary for an assistant to the president, $183,000.
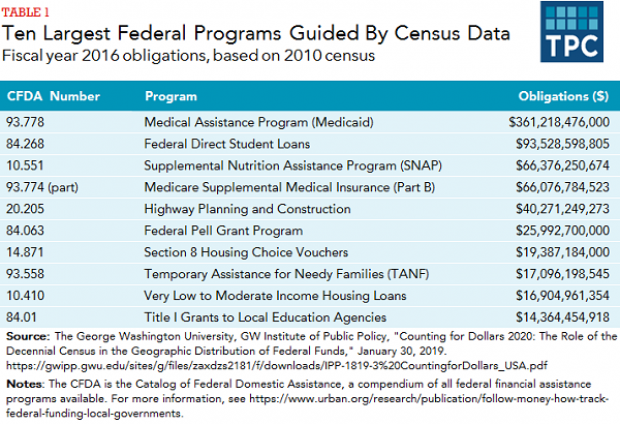
The Census Affects Nearly $1 Trillion in Spending

The 2020 census faces possible delay as the Supreme Court sorts out the legality of a controversial citizenship question added by the Trump administration. Tracy Gordon of the Tax Policy Center notes that in addition to the basic issue of political representation, the decennial population count affects roughly $900 billion in federal spending, ranging from Medicaid assistance funds to Section 8 housing vouchers. Here’s a look at the top 10 programs affected by the census:
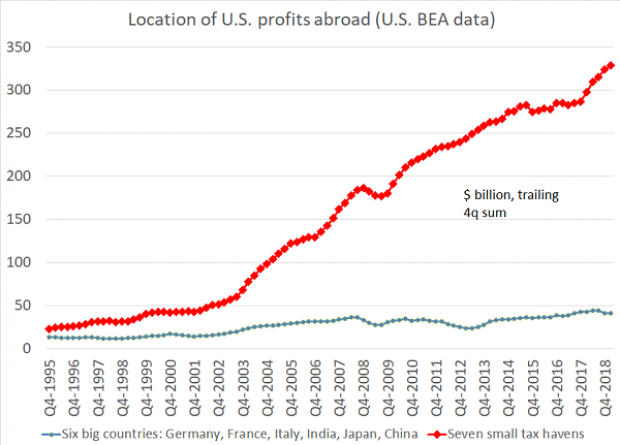
Chart of the Day: Offshore Profits Continue to Rise

Brad Setser, a former U.S. Treasury economist now with the Council on Foreign Relations, added another detail to his assessment of the foreign provisions of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act: “A bit more evidence that Trump's tax reform didn't change incentives to offshore profits: the enormous profits that U.S. firms report in low tax jurisdictions continues to rise,” Setser wrote. “In fact, there was a bit of a jump up over the course of 2018.”