You Won’t Believe How Much Diabetes is Costing the U.S.
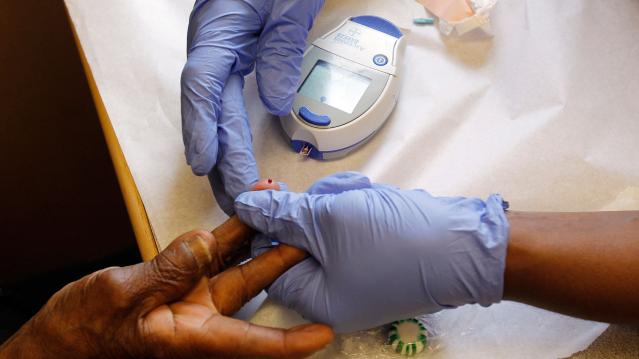
The budget-busting price of Sovaldi, a drug used to treat hepatitis C has generated wave after wave of media attention, but it’s far from the only drug creating cost problems for patients and insurers.
As Michelle Andrews of Kaiser Health News points out, diabetes affects 29 million Americans, or 10 times as many people as hepatitis C, and the costs of treating it have been rising quickly. And because it’s a chronic condition, people require lifetime care.
Related: Diabetes Detection Up in Pro-Obamacare States
In 2011, the average annual health spending for individuals with diabetes was $14,093. Two years later, it had risen to $14,999, according to the Healthcare Cost Institute. In contrast, a person without diabetes spent about $10,000 less in medical costs in 2013. Pharmacy provider Express Scripts said earlier this year that 2014 marked the fourth year in a row that medication used to treat diabetes were the most expensive of any traditional drug class.
In all, diabetes costs totaled an estimated $245 billion in 2012, including both direct medical expenses and indirect costs from disability and lost work productivity.
While some of the most popular diabetes drugs aren’t particularly expensive, the new brand-name drugs that are continually being introduced offer more effective treatment and fewer side effects — but also come with a higher price tag. Less than half of the diabetes prescription treatments filled in 2014 were generic.
Nearly a century after its discovery in 1921, insulin is still a common form of treatment for the millions of people with type 1 diabetes, yet there is still no generic form available. Patent protection has been extended in some cases due to improvements in existing formulations. Once those patents expire, Andrews notes, biologically similar drugs could replace them and reduce the price by up to 40 percent.
Related: This Disease Hikes Health Care Costs By More than $10,000 a Year
The financial ramifications of diabetes don’t just stem from the cost of drugs or medical treatment — it’s also been proven that people with diabetes have a high-school dropout rate that is six percentage points higher than those without the disease, according to a Health Affairs study. In addition, young adults with diabetes are four to six percentage points less likely to attend college than those without the disease.
Diabetes also contributes to lower employment and wages. On average, a person with diabetes earns $160,000 less over the course of their lives than people who don’t develop the disease. By age 30, a person with diabetes is 10 percent less likely to be employed.
So even if it’s not generating as many headlines as hepatitis C at any given point in time, the costs of diabetes can’t be ignored.
Top Reads From The Fiscal Times
- The 10 Worst States for Property Taxes
- Two-Thirds of Americans Believe Social Security Is in a Crisis State
- Why McDonald’s Could Suddenly Be Responsible for Millions of New Employees
Watch Lindsey Graham Destroy His Phone, Get a Bit of Revenge on Donald Trump

What do you do when Donald Trump gives out your cellphone number in a televised campaign rally? South Carolina Sen. Lindsey Graham, a Trump rival for the GOP presidential nomination, made the most of The Donald’s rude move by releasing a video in which he demolishes his phone (more than one, actually) by doing everything short of blowing it up.
Related: 7 Revelations from Donald Trump’s Financial Disclosure
The YouTube video, posted by IJ Review and titled “How to Destroy Your Phone With Sen. Lindsey Graham,” shows the senator smashing a Samsung flip phone in various ways — a golf club, a wooden sword, a cinder block — and also chopping it with a meat cleaver, putting it in a toaster oven with pizza bagels, dropping it in a blender with some Red Bull, lighting it on fire and dropping it from a rooftop.
“Or if all else fails, you can always give your number to The Donald,” Graham says toward the end of the 1:04 clip.
Related: The 2016 Presidential Election Is Already a Dumpster Fire
Graham isn’t exactly a technophile, so maybe he didn’t know he didn’t need to destroy his phone to get a new number (and there are much better ways to get rid of an old phone). More likely, though, the senator found a clever way to take advantage of the attention Trump provided for him and his campaign while also finally upgrading from his flip phone to a smartphone.
Probably getting a new phone. iPhone or Android?
— Lindsey Graham (@LindseyGrahamSC) July 21, 2015
Graham has struggled to make headway in a crowded Republican presidential field, drawing the support of less than 1 percent of registered GOP voters in recent polls. That would leave him off the stage in the Aug. 6 Fox News debate, which is limited to 10 of the 16 candidates. Trump, by the way, is almost assured of a spot. So the senator and his campaign need all the attention they can get — and the new video sure is getting attention. Since it was published to YouTube yesterday, it’s already been viewed more than 1 million times.
McDonald’s McTricks Aren’t Working

Turns out warm buns aren’t the solution to McDonald’s financial woes.
The burger giant announced Thursday that its sales slide continued in the second quarter, with same store sales falling 0.7 percent globally and by 2 percent in the U.S. Quarterly revenues dropped 10 percent to $6.5 billion, though without currency effects from a strong dollar they would have climbed 1 percent.
The results were good enough to top Wall Street’s expectations, but they showed again just how far McDonald’s has to go to win back customers.
Related: The 11 Worst Fast Food Restaurants in America
The fast food chain blamed the admittedly “disappointing” results on the failure of its products and promotions to draw customers to its stores as anticipated.
New CEO Steve Easterbrook, who took over in March, has promised to revamp the restaurant chain and improve sales by catering to consumers who prefer fresh, high quality food.
McDonald’s continues to try a variety of promotions and menu changes to win back diners. It recently started offering a double cheeseburger and fries for $2.50 as a summer deal and rolled out an “artisan grilled chicken sandwich.” It has also, among other things, enlarged its quarter pounder, tested a new breakfast bowl full of kale, rolled out flavored hot coffee in some locations and even tested a lobster roll in New England restaurants. And it upped the toasting time for its hamburger buns by 5 seconds.
So far, though, the new deals and menu options have failed to entice diners.
Related: 9 Ways McDonald’s Wants to Get You Excited About Its Food Again
Easterbrook did acknowledge that changing McDonalds’ image would take time, but he said Thursday that the company is “seeing early signs of momentum.”
The company will begin to offer all-day breakfast, which already accounts for 25 percent of the company’s sales. And it is continuing to simplify its menu options to lower costs.
Analysts wonder if such changes will be enough to boost consumer appetites for McDonald’s and how the company is going to reposition its brand. As Thursday earnings report made clear, introducing a younger, hip hamburglar isn’t going to cut it.
Why Shark Attacks Have a Silver Lining

While recent headlines about the above average number of shark attacks in the U.S. this year may have rethinking your summer vacation, the incidents could be good news for the ocean’s ecosystem.
Conservation measures implemented to prevent the decline of great white sharks are paying off, scientists have found. The global population of great whites has been in recovery since 1990.
One of the key components in this environmental success story is the passage of the Marine Mammal Protection Act in 1972. With the legislation, seal and sea lion populations began to rebound along the West Coast. Great white sharks eat both seals and sea lions and having more food available most likely boosted their comeback.
A healthy shark population makes for a more balanced ecosystem, leading to healthier oceans that support all lives, both human and non-human. Oceans produce over half of the oxygen in the atmosphere and absorb the majority of carbon in it.
The increase in the number of sharks suggests that some of the damage humans have caused in the oceans has been reversed. However, it will take a while for sharks to rebuild their populations completely. It takes sharks at least eight years to reach a reproductive age and gestation periods can last 18 months.
Even though “Sharknado: Oh Hell No!” is getting awful reviews this week, everyone should applaud this other bit of shark-related news.
Teens Are Having Much Less Sex Than Their Parents Did at That Age

Adolescents may be thinking about sex all the time, but fewer teens are actually doing the deed. Since 1988, sex has dropped by 14 percent among teenage females (ages 15 to 19) and 22 percent among teenage males (ages 15 to 19). The latest study from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Health Statistics shows that 44 percent of female teenagers and 47 percent of male teenagers had experienced sexual intercourse at least once.
Related: The App-Selling Power of Kate Upton’s Cleavage
The good news? The majority of them used contraception. From 2011 to 2013, 79 percent of female teenagers and 84 percent of male teenagers used contraception the first time they had sexual intercourse. Condoms were the most widely used method of contraception among teenage girls, followed by withdrawal (60 percent) and the pill (54 percent). Use of the emergency “Plan B” or “morning after pill” came in fourth, reaching 22 percent in 2013, and up from 8 percent in 2002.
About 70 percent of 15- to 19-year-old females said their first sexual intercourse happened with a steady dating partner, compared to about 50 percent of 15- to 19-year-old males.
Could all that sex education be working? Are teenagers watching more porn? Do teens have more access to contraception because of Obamacare? Then again, it could be all those episodes of reality TV they’re watching. Last year CNN reported a study from the National Bureau of Economic Research that linked watching MTV’s 16 and Pregnant and Teen Mom to a 5.7 percent reduction in teen births in the U.S. The study found a correlation between higher rates of viewership in certain areas with a bigger decrease in teen births.
Related: Schools Gamble on Gut-Punch Anti-Drug Programs for Teens
Despite teen births being at an all-time low, the U.S. still leads other developed countries in teen pregnancy. (New Zealand comes in second, followed by England and Wales.) And if parents are worried their teens won’t ever get off their iPhones long enough to have sex, they can relax. Most teens, or two-thirds of adolescents, will have sex by the time they’re 19.
Here’s a Good Sign for the Economy: Americans Are Hitting the Road

Driving is as American as apple pie, but the Great Recession took a big bite out of the nation’s driving habits. Total miles driven in the U.S. hit a peak in the fall of 2007 just before the recession hit and fell for several years after. Total miles driven bottomed out in 2011, moving slowly higher since then.
The Department of Transportation reported this week that total miles driven has hit a new, all-time high. Vehicles drove 7.3 billion miles in May, up 2.7 percent from May, 2014. The annual number is even more impressive: Using a moving 12-month figure, total miles traveled in the past year registers at 3.08 trillion miles. This graph from Calculated Risk paints the picture:

This sure seems like good news for the U.S. economy. The data for miles driven reflects booms and busts in the economy, and seeing the numbers climb suggests the economy is still gaining strength.
However, the raw numbers may not be quite as good as they first appear. Even though miles driven are up, so is the U.S. population. Once the data is adjusted for population growth, a less robust picture emerges. Doug Short at Advisor Perspectives ran the numbers, concluding that on a per capita basis, miles driven is still well below its pre-recession peak. Here’s his chart:

It looks like the U.S. economy still has a long way to go to get back to its pre-recession strength, at least as measured by by the rough proxy of total miles driven.
