Why Millennials Are Waiting So Long to Buy Their First Homes

They may finally be moving out of their parents’ basements, but don’t expect those boomerang kids to be taking out a mortgage any time soon.
Today’s first-time homebuyer rents for an average of six years before buying his or her first home, according to a new analysis by Zillow. Time spent renting has been marching mostly upward since the 1970s, when first-time buyers rented for just 2.6 years before purchasing a home.
Today’s first-time buyers are also more likely to be single and older (with an average age of 32.5) than previous generations.
“Millennials are delaying all kinds of major life decisions, like getting married and having kids, so it makes sense that they would also delay buying a home,” Zillow Chief Economist Svenja Gudell said in a statement.
Related: Found Your Dream Home? 7 Tips for Getting the Best Deal
Part of the reason for that delay could be that homes cost much more than they did decades ago. Today’s homebuyer makes roughly the same amount of money in inflation-adjusted terms as a buyer in the 1970s, but the homes that they’re purchasing are about 60 percent more expensive.
There are other roadblocks for first-timers. Limited inventory and strong competition make the home buying process difficult for property virgins and student debt can make it tougher to get a mortgage.
Those six years spent renting aren’t coming cheap, either. In 2013, almost half of all renters were spending more than 30 percent of their income on housing, with more than a quarter sending half their income to their landlord every month, according to the “State of the Nation’s Housing 2015” report issued in June by the Harvard Joint Center for Housing Studies. That makes it pretty tough to save for a down payment.
Top Reads from the Fiscal Times:
- Trump as Commander in Chief? Tune in for a Foreign Policy Reality Show
- Clinton’s Email Fail May Be Innocent, but Americans Still Don’t Trust Her
- As Obamacare Costs Rise, the GOP Has a Real Chance to Reform Health Care
Economists See More Growth Ahead

Most business economists in the U.S. expect the economy to keep chugging along over the next three months, with rising corporate sales driving additional hiring and wage increases for workers.
The tax cuts, however, don’t seem to be playing a role in hiring and investment plans. And the trade conflicts stirred up by the Trump administration are having a negative influence, with the majority of economists at goods-producing firms who replied to the most recent survey by the National Association for Business Economics saying that their companies were putting investments on hold as they wait to see how things play out.
New Tax on Non-Profits Hits Public Universities

The Republican tax bill signed into law late last year imposed a 21 percent tax on employees at non-profits who earn more than $1 million a year. According to data from the Chronicle of Higher Education cited by Bloomberg, there were 12 presidents of public universities who received compensation of at least $1 million in 2017, with James Ramsey of the University of Louisville topping the list at $4.3 million. Endowment managers could also get hit with the tax, as could football coaches, some of whom earn substantially more than the presidents of their institutions.
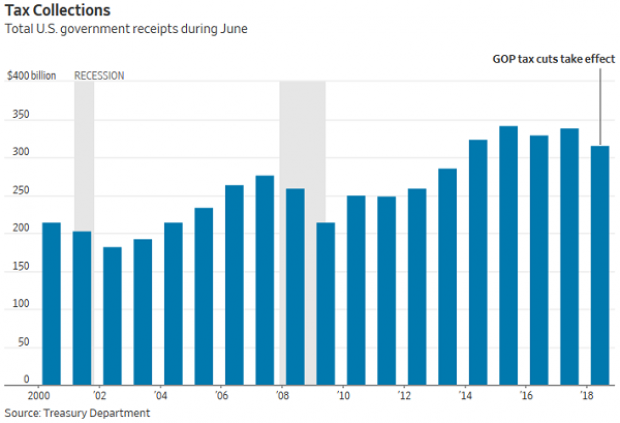
Government Revenues Drop as Tax Cuts Kick In

Corporate tax receipts in June were 33 percent lower than a year ago, according to data released by the Treasury Department Thursday, as companies made smaller estimated payments due to the reduction in their tax rates. Total receipts were down 7 percent, while payroll taxes were 5 percent lower compared to June 2017.
“June receipts to US government were our first mostly-clear look at the revenue effects of the new tax law, with lots of estimated payments and little noise from the 2017 tax year,” The Wall Street Journal’s Richard Rubin tweeted Friday.
Surprisingly, the deficit was smaller in June compared to a year ago, narrowing to $74.86 billion from $90.23 billion last year. The drop was driven by a 9 percent reduction in government outlays that reflected accounting changes rather than any real changes in spending, Rubin said in the Journal.
“More broadly, the federal deficit is swelling as government spending outpaces revenues,” Rubin wrote. “The budget gap totaled $607.1 billion in the first nine months of the 2018 fiscal year, 16% larger than the same point a year earlier.”
Kyle Pomerleau of the Tax Foundation pointed out that the drop in corporate tax receipts is a permanent feature of the Republican tax cuts, tweeting: “Even in a Trump dream world in which these cuts paid for themselves, corporate tax collections would remain below baseline forever. It would be higher income and payroll receipts that made up the difference.”
Deficit Jumps in Trump’s First Fiscal Year

The federal budget deficit rose by 16 percent in the first nine months of the 2018 fiscal year, which began last October. The shortfall came to $607 billion, compared to $523 billion in the same period the year before, according to a U.S. Treasury report released Thursday and reported by Bloomberg. Both revenue and spending rose, but spending rose faster. Revenues came to $2.54 trillion, up 1.3 percent from the same nine-month period in 2017, while spending came to $3.15 trillion, up 3.9 percent.
Where’s the Obamacare Navigator Funding for 2019, PA Insurance Commissioner Asks
Pennsylvania’s insurance commissioner sent a letter this week to Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar and Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Administrator Seema Verma requesting that they “immediately release the funding details for the Navigator program for the upcoming open enrollment period for 2019.” Navigators are the state and local groups that help people sign up for Affordable Care Act plans.
“In years past, grant applications and new funding opportunities were released by CMS in April, CMS required Navigator organizations to apply by June and approved applications and new funding by late August,” Pennsylvania’s Jessica Altman wrote. “The current lack of guidance has put Navigator organizations – and states - far behind in their planning and creates an inability for the Navigator organizations to design a successful plan for helping people enroll during the 2019 open enrollment period.”