Why Millennials Are Waiting So Long to Buy Their First Homes

They may finally be moving out of their parents’ basements, but don’t expect those boomerang kids to be taking out a mortgage any time soon.
Today’s first-time homebuyer rents for an average of six years before buying his or her first home, according to a new analysis by Zillow. Time spent renting has been marching mostly upward since the 1970s, when first-time buyers rented for just 2.6 years before purchasing a home.
Today’s first-time buyers are also more likely to be single and older (with an average age of 32.5) than previous generations.
“Millennials are delaying all kinds of major life decisions, like getting married and having kids, so it makes sense that they would also delay buying a home,” Zillow Chief Economist Svenja Gudell said in a statement.
Related: Found Your Dream Home? 7 Tips for Getting the Best Deal
Part of the reason for that delay could be that homes cost much more than they did decades ago. Today’s homebuyer makes roughly the same amount of money in inflation-adjusted terms as a buyer in the 1970s, but the homes that they’re purchasing are about 60 percent more expensive.
There are other roadblocks for first-timers. Limited inventory and strong competition make the home buying process difficult for property virgins and student debt can make it tougher to get a mortgage.
Those six years spent renting aren’t coming cheap, either. In 2013, almost half of all renters were spending more than 30 percent of their income on housing, with more than a quarter sending half their income to their landlord every month, according to the “State of the Nation’s Housing 2015” report issued in June by the Harvard Joint Center for Housing Studies. That makes it pretty tough to save for a down payment.
Top Reads from the Fiscal Times:
- Trump as Commander in Chief? Tune in for a Foreign Policy Reality Show
- Clinton’s Email Fail May Be Innocent, but Americans Still Don’t Trust Her
- As Obamacare Costs Rise, the GOP Has a Real Chance to Reform Health Care
The High Cost of Child Poverty

Childhood poverty cost $1.03 trillion in 2015, including the loss of economic productivity, increased spending on health care and increased crime rates, according to a recent study in the journal Social Work Research. That annual cost represents about 5.4 percent of U.S. GDP. “It is estimated that for every dollar spent on reducing childhood poverty, the country would save at least $7 with respect to the economic costs of poverty,” says Mark R. Rank, a co-author of the study and professor of social welfare at Washington University in St. Louis. (Futurity)
Do You Know What Your Tax Rate Is?

Complaining about taxes is a favorite American pastime, and the grumbling might reach its annual peak right about now, as tax day approaches. But new research from Michigan State University highlighted by the Money magazine website finds that Americans — or at least Michiganders — dramatically overstate their average tax rate.
In a survey of 978 adults in the Wolverine State, almost 220 people said they didn’t know what percentage of their income went to federal taxes. Of the people who did provide an answer, almost 85 percent overstated their actual rate, sometimes by a large margin. On average, those taxpayers said they pay 25.5 percent of their income in federal taxes. But the study’s authors estimated that their actual average tax rate was just under 14 percent.
The large number of people who didn’t want to venture a guess as to their tax rate and the even larger number who were wildly off both suggest to the researchers “that a very substantial portion of the population is uninformed or misinformed about average federal income-tax rates.”
Why don’t we know what we’re paying?
Part of the answer may be that our tax system is complicated and many of us rely on professionals or specialized software to prepare our filings. Money’s Ian Salisbury notes that taxpayers in the survey who relied on that kind of help tended to be further off in their estimates, after controlling for other factors.
Also, many people likely don’t understand the different types of taxes they pay. While the survey asked specifically about federal taxes, the tax rates people provided more closely matched their total tax rate, including federal, state, local and payroll taxes.
But our politics likely play a role here as well. People who believe that taxes on households like theirs should be lower and those who believe tax dollars are spent ineffectively tended to overstate their tax rates more.
“Since the time of Ronald Reagan, American[s] have been inundated with messages about how high taxes are,” one of the study’s authors told Salisbury. “The notion they are too high has become deeply ingrained.”
Wealthy Investors Are Worried About Washington, and the Debt
A new survey by the Spectrem Group, a market research firm, finds that almost 80 percent of investors with net worth between $100,000 and $25 million (not including their home) say that the U.S. political environment is their biggest concern, followed by government gridlock (76 percent) and the national debt (75 percent).
Trump’s Push to Reverse Parts of $1.3 Trillion Spending Bill May Be DOA
At least two key Republican senators are unlikely to support an effort to roll back parts of the $1.3. trillion spending bill passed by Congress last month, The Washington Post’s Mike DeBonis reported Monday evening. While aides to President Trump are working with House Majority Leader Kevin McCarthy (R-CA) on a package of spending cuts, Sens. Susan Collins (R-ME) and Lisa Murkowski (R-AK) expressed opposition to the idea, meaning a rescission bill might not be able to get a simple majority vote in the Senate. And Roll Call reports that other Republican senators have expressed significant skepticism, too. “It’s going nowhere,” Sen. Lindsey Graham said.
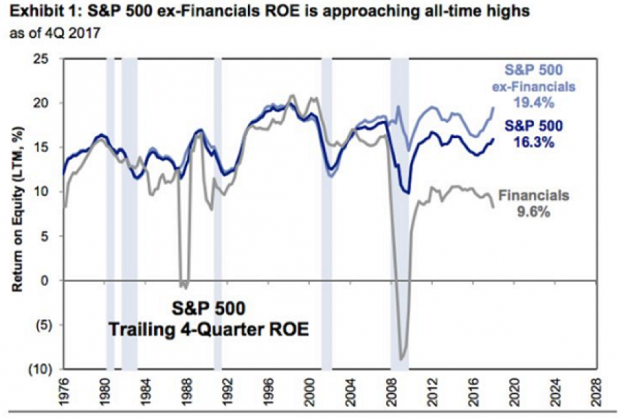
Goldman Sees Profit in the Tax Cuts
David Kostin, chief U.S. equity strategist at Goldman Sachs, said in a note to clients Friday cited by CNBC that companies in the S&P 500 can expect to see a boost in return on equity (ROE) thanks to the tax cuts. Return on equity should hit the highest level since 2007, Kostin said, providing a strong tailwind for stock prices even as uncertainty grows about possible conflicts over trade.
Return on equity, defined as the amount of net income returned as a percentage of shareholders’ equity, rose to 16.3 percent in 2016, and Kostin is forecasting an increase to 17.6 percent in 2018. "The reduction in the corporate tax rate alone will boost ROE by roughly 70 [basis points], outweighing margin pressures from rising labor, commodity, and borrow costs," Kostin wrote.