Americans Are Happier with This Car Brand Than Any Other

Americans may love their cars, but these days they love them a little less.
Consumer satisfaction with their cars has fallen for the third consecutive year, reflecting unhappiness with increasing recalls and rising prices, according to new data from the American Customer Satisfaction Index.
Car reliability has improved overall in the past decade but the number of recalls is at an all-time high. “This should not happen with modern manufacturing technology and has negative consequences for driver safety, costs, and customer satisfaction,” ACSI Chairman and founder Claes Fornell said in a statement.
Car owners in the second quarter of 2015 reported a 40 percent increase in recalls year over year. The most high profile recalls involve Takata airbags, affecting more than 17 million older-model vehicles built by 11 different auto makers.
Related: Senators Urge Recall of All Vehicles with Takata Airbags
Looking at individual brands, the index shows that Americans prefer Japanese and luxury brand cars, with Lexus displacing Mercedes Benz as the brand with the highest overall satisfaction (84 out of 100). Mercedes tied for second place with Acura and Lincoln.
The average for all autos fell 3.7 points to 79. The only American automaker to rank above average was Ford with a score of 81. General Motors and Chrysler saw their scores fall modestly to 79 and 75 respectively.
Despite a growing decline in satisfaction, Americans are holding onto their vehicles longer than ever. The average age of cars and light trucks is now 11.5 years old, according to a report issued last month by IHS Automotive.
Top Reads from the Fiscal Times:
- Big Surprise: Hispanic Voters Can’t Stand Donald Trump
- How a Biden-Warren Ticket Could Transform the Campaign
- Air Force Brushes Off $27 Billion Accounting Error
Why Craft Brewers Are Crying in Their Beer

It may be small beer compared to the problems faced by unemployed federal workers and the growing cost for the overall economy, but the ongoing government shutdown is putting a serious crimp in the craft brewing industry. Small-batch brewers tend to produce new products on a regular basis, The Wall Street Journal’s Ruth Simon says, but each new formulation and product label needs to be approved by the Treasury Department’s Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau, which is currently closed. So it looks like you’ll have to wait a while to try the new version of Hemperor HPA from Colorado’s New Belgium Brewing, a hoppy brew that will include hemp seeds once the shutdown is over.
Number of the Day: $30 Billion
The amount spent on medical marketing reached $30 billion in 2016, up from $18 billion in 1997, according to a new analysis published in the Journal of the American Medical Association and highlighted by the Associated Press. The number of advertisements for prescription drugs appearing on television, newspapers, websites and elsewhere totaled 5 million in one year, accounting for $6 billion in marketing spending. Direct-to-consumer marketing grew the fastest, rising from $2 billion, or 12 percent of total marketing, to nearly $10 billion, or a third of spending. “Marketing drives more treatments, more testing” that patients don’t always need, Dr. Steven Woloshin, a Dartmouth College health policy expert and co-author of the study, told the AP.
70% of Registered Voters Want a Compromise to End the Shutdown

An overwhelming majority of registered voters say they want the president and Congress to “compromise to avoid prolonging the government shutdown” in a new The Hill-HarrisX poll. Seven in ten respondents said they preferred the parties reach some sort of deal to end the standoff, while 30 percent said it was more important to stick to principles, even if it means keeping parts of the government shutdown. Voters who “strongly approve” of Trump (a slim 21 percent of respondents) favored him sticking to his principles over the wall by a narrow 54 percent-46 percent margin. Voters who “somewhat approve” of the president favored a compromise solution by a 70-30 margin. Among Republicans overall, 61 percent said they wanted a compromise.
The survey of 1,000 registered voters was conducted January 5 and 6 and has a margin of error of 3.1 percentage points.
Share Buybacks Soar to Record $1 Trillion

Although there may be plenty of things in the GOP tax bill to complain about, critics can’t say it didn’t work – at least as far as stock buybacks go. TrimTabs Investment Research said Monday that U.S. companies have now announced $1 trillion in share buybacks in 2018, surpassing the record of $781 billion set in 2015. "It's no coincidence," said TrimTabs' David Santschi. "A lot of the buybacks are because of the tax law. Companies have more cash to pump up the stock price."
Chart of the Day: Deficits Rising
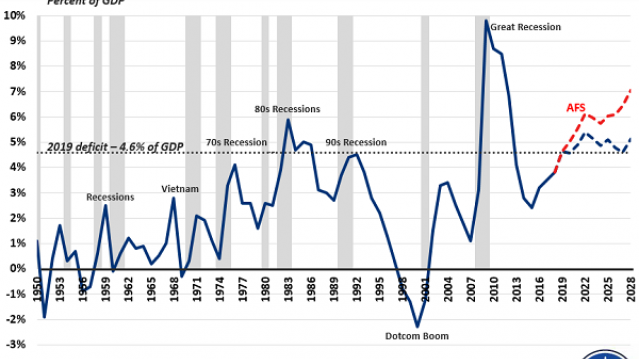
Budget deficits normally rise during recessions and fall when the economy is growing, but that’s not the case today. Deficits are rising sharply despite robust economic growth, increasing from $666 billion in 2017 to an estimated $970 billion in 2019, with $1 trillion annual deficits expected for years after that.
As the deficit hawks at the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget point out in a blog post Thursday, “the deficit has never been this high when the economy was this strong … And never in modern U.S. history have deficits been so high outside of a war or recession (or their aftermath).” The chart above shows just how unusual the current deficit path is when measured as a percentage of GDP.
