How the Stock Market’s Wild Swings Have Helped Homebuyers

The rollercoaster week on Wall Street could pay off nicely for some homebuyers.
The sharp selloff in global markets, caused by the economic uncertainty in China, caused investors running for safety to buy up U.S. government bonds, driving interest rates down. That sent the rate on benchmark 30-year fixed-rate mortgages down to its lowest level since May.
Related: The Financial Mistake That Can Cost Homeowners
Mortgage giant Freddie Mac said Thursday that the average for 30-year fixed-rate loans fell to 3.84 percent, with an average 0.6 points, over the week ending August 27. That’s down from 3.93 percent last week and 4.10 percent a year ago. For 15-year fixed-rate loans, the average was 3.06 percent, down from 3.15 percent last week and 3.25 percent a year ago.
The average on 30-year fixed-rate mortgages has now been below 4 percent for five straight weeks. Just how long they stay there will be determined in part by when the Federal Reserve decides to raise interest rates for the first time since 2006. Many economists had expected the Fed to raise rates next month — but that was before the stock market’s latest shakeup.
"There are indications, though, that the unsettled state of global markets will make the Fed think twice before taking any action on short-term interest rates in September,” Sean Becketti, Freddie Mac’s chief economist, said in a statement. “If that's the case, the 30-year mortgage rate may remain subdued in the short-to-medium term, providing support for continued strength in the housing sector."
Related: Rate-Hike Havoc: Can the Fed Ignore This Market Rout?
Greg McBride, chief financial analyst with Bankrate.com, said mortgage rates may trend a bit higher from here as financial markets settle down, but he added that the Fed’s hike, whenever it comes, isn’t going to dramatically affect mortgage rates that are still historically low.
“That the initial move by the Fed is to a large extent already reflected in mortgage rates,” McBride said. “You might see a little bit of a further bump, but not much. Mortgage rates are not going to skyrocket. That’s the main point. Increases that we see in mortgage rates in the coming months are likely to be very limited."
Top Reads From The Fiscal Times
- The Troubling Truth Revealed by the Stock Market’s Nosedive
- Mark Cuban: The Lesson Investors Can Learn From China
- Why China’s Slowdown Will Lead to Sustainable Growth
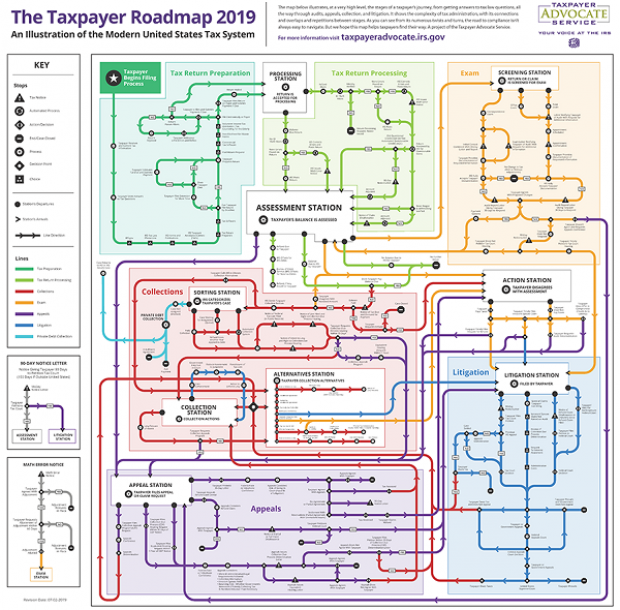
Map of the Day: Navigating the IRS

The Taxpayer Advocate Service – an independent organization within the IRS whose roughly 1,800 employees both assist taxpayers in resolving problems with the tax collection agency and recommend changes aimed at improving the system – released a “subway map” that shows the “the stages of a taxpayer’s journey.” The colorful diagram includes the steps a typical taxpayer takes to prepare and file their tax forms, as well as the many “stations” a tax return can pass through, including processing, audits, appeals and litigation. Not surprisingly, the map is quite complicated. Click here to review a larger version on the taxpayer advocate’s site.
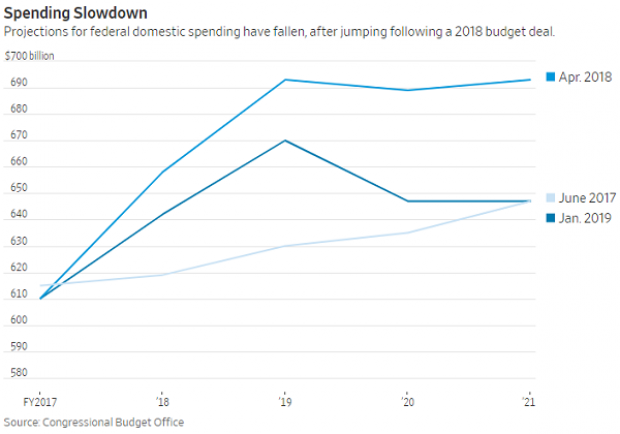
A Surprise Government Spending Slowdown

Economists expected federal spending to boost growth in 2019, but some of the fiscal stimulus provided by the 2018 budget deal has failed to show up this year, according to Kate Davidson of The Wall Street Journal.
Defense spending has come in as expected, but nondefense spending has lagged, and it’s unlikely to catch up to projections even if it accelerates in the coming months. Lower spending on disaster relief, the government shutdown earlier this year, and federal agencies spending less than they have been given by Congress all appear to be playing a role in the spending slowdown, Davidson said.
Number of the Day: $203,500

The Wall Street Journal’s Catherine Lucey reports that acting White House Chief of Staff Mick Mulvaney is making a bit more than his predecessors: “The latest annual report to Congress on White House personnel shows that President Trump’s third chief of staff is getting an annual salary of $203,500, compared with Reince Priebus and John Kelly, each of whom earned $179,700.” The difference is the result of Mulvaney still technically occupying the role of director of the White House Office of Management and Budget, where his salary level is set by law.
The White House told the Journal that if Mulvaney is made permanent chief of staff his salary would be adjusted to the current salary for an assistant to the president, $183,000.
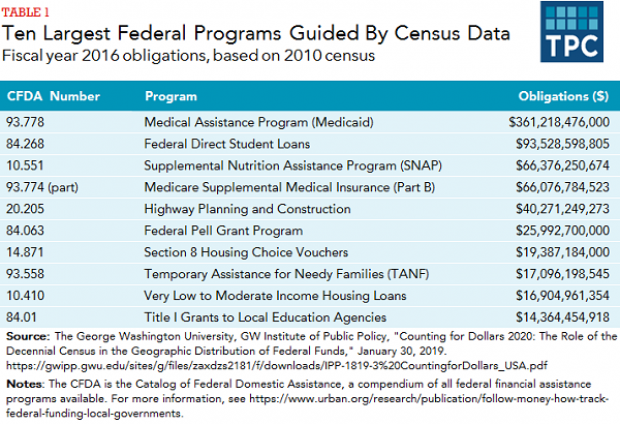
The Census Affects Nearly $1 Trillion in Spending

The 2020 census faces possible delay as the Supreme Court sorts out the legality of a controversial citizenship question added by the Trump administration. Tracy Gordon of the Tax Policy Center notes that in addition to the basic issue of political representation, the decennial population count affects roughly $900 billion in federal spending, ranging from Medicaid assistance funds to Section 8 housing vouchers. Here’s a look at the top 10 programs affected by the census:
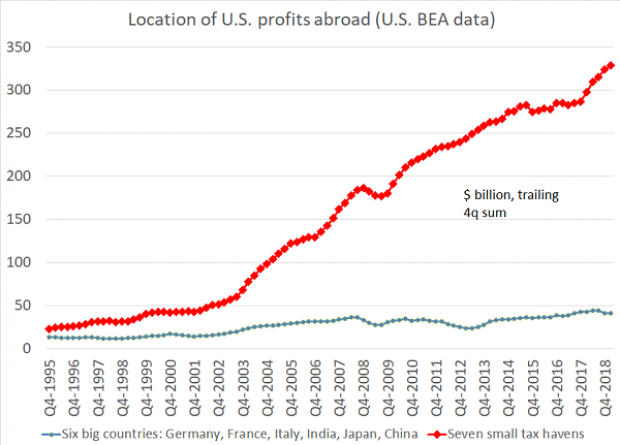
Chart of the Day: Offshore Profits Continue to Rise

Brad Setser, a former U.S. Treasury economist now with the Council on Foreign Relations, added another detail to his assessment of the foreign provisions of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act: “A bit more evidence that Trump's tax reform didn't change incentives to offshore profits: the enormous profits that U.S. firms report in low tax jurisdictions continues to rise,” Setser wrote. “In fact, there was a bit of a jump up over the course of 2018.”