Jeb Bush Fires Back at Trump, but Is Anyone Listening?

Despite the sizzling Summer of Trump, Jeb Bush and the rest of the Republican establishment still don’t get it.
Bush just released an 80-second video entitled “The Real Donald Trump”, as flagged by Mike Allen in his Politico Playbook note this morning, in a slick effort to attack Trump by using his own words against him. That’s a classic campaign tactic, of course, and the effort by the Bush campaign is aimed at painting the bombastic real estate mogul from New York as a fake conservative – someone whose core values and views are anathema to Republicans in Iowa, where the Real Clear Politics poll average puts Trump in the lead for the GOP Caucuses with 21.3 percent.
Related: Two New Polls Show Exactly Why Donald Trump Is Winning
Here’s a sampling from the video:
Talking to Tim Russert on Meet the Press, 1999:
- “I’ve lived in New York City and Manhattan all my life, so you know my views are a little bit different than if I lived in Iowa.”
- “I am very pro-choice. I am pro-choice in every respect.”
From a 1999 Fox News clip:
- “As far as single-payer [heathcare system], it works in Canada. It works incredibly well in Scotland.”
Talking to Wolf Blitzer on CNN:
- Who would you like representing the United States in a deal with Iran? “I think Hillary would do a good job.”
- Do you identify more as a Democrat or a Republican? “Well, you’d be shocked if I said that in many cases I probably identify more as a Democrat.”
From a 2001 Fox News clip:
- “Hillary Clinton is a terrific woman. I’m a little biased because I’ve known her for years.”
Some of the clips are 15 years old or older and show Trump for what he was: a New Yorker with unremarkable New York liberal/centrist positions on a lot of issues.
Related: Fiorina PAC: CNN and GOP Are Conspiring Against Carly
The big question for Bush and other Republican politicians in the race is: Does it matter that much where Trump once stood or even where he now stands? If it doesn’t, that is going to make taking him down even more difficult.
What Trump is selling is unvarnished authenticity to an electorate tired of politicians who try to be all things to all people. You’re not going to catch Trump courting the gun crowd by saying he likes to hunt small varmints, like the patrician Mitt Romney did. Or donning a Rocky the Squirrel hat and riding around in a tank like Mike Dukakis did in 1988 to try to show he could be a credible commander-in-chief.
Mad-as-hell voters are sick of phoniness and goofy photo ops. When will the career politicians get that?
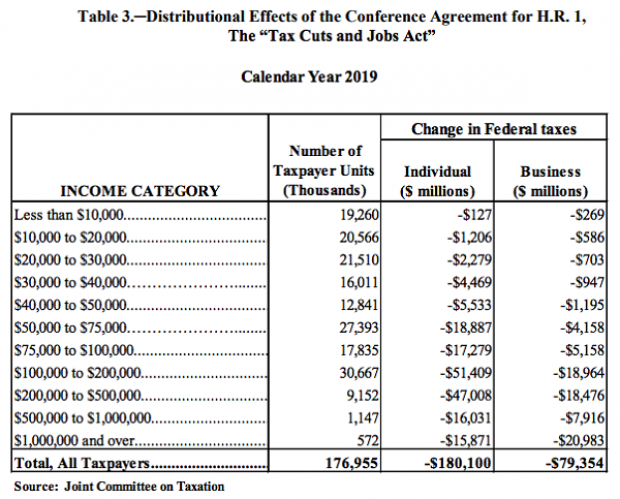
Majority of Tax Cuts Going to Filers Earning More Than $100K: JCT

Ahead of a House Ways and Means Committee hearing scheduled for Wednesday, the Joint Committee on Taxation prepared an analysis of the distributional effects of the 2017 Republican tax bill. The New York Times’ Jim Tankersley highlighted the fact that according to the JCT analysis, about 75 percent of the individual and business benefits of the tax cuts will go to filers earning more than $100,000 in 2019. And nearly half of the benefits will flow to filers earning over $200,000.
The Trump Budget's $1.2 Trillion in 'Phantom Revenues'

President Trump’s 2020 budget includes up to $1.2 trillion in “potentially phantom revenues” — money that comes from taxes the administration opposes or from tax hikes that face strong opposition from businesses, The Wall Street Journal’s Richard Rubin reports, citing data from the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget. That total, covering 2020 through 2029, includes as much as $390 billion in taxes created under the Affordable Care Act, which the president wants to repeal.
The $1.2 trillion in questionable revenue projections is in addition to the White House budget’s projected deficits of $7.3 trillion for the 10-year period. That total is itself questionable, given that the president’s budget relies on optimistic assumptions about economic growth and some unrealistic spending cuts, meaning that the deficits could be significantly higher than projected.
Republicans Push Ahead on Medicaid Restrictions

The Trump administration on Friday approved Ohio’s request to impose work requirements on Medicaid recipients. Starting in 2021, the state will require most able-bodied adults aged 19 to 49 to either work, go to school, be in job training or volunteer for 80 hours a month in order to receive Medicaid benefits. Those who fail to meet the requirements over 60 days will be removed from the system, although they can reapply immediately.
The new work requirements include exemptions for pregnant women, caretakers and those living in counties with high unemployment rates and will apply only to those covered through the expansion of Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act. There are currently about 540,000 people on Medicaid in Ohio who receive coverage through the expansion, according to Kaitlin Schroeder of The Dayton Daily News, compared to roughly 2.6 million Medicaid recipients in the state overall.
Once implemented, the work requirements are expected to result in 36,000 people losing their Medicaid eligibility, according to state officials, though critics say the reductions could be significantly larger. Similar work requirements in Arkansas pushed 18,000 people off the Medicaid rolls in six months.
A larger GOP project: The creation of new work requirements is part of a larger effort by Republicans to limit the expansion of Medicaid, says The Wall Street Journal’s Stephanie Armour. Since the Affordable Care Act passed in 2010, 36 states have expanded their Medicaid programs under the ACA and the number of people in the program has grown by 50 percent, from roughly 50 million to about 75 million. But many red-state governors have expressed concerns about the cost of Medicaid expansion and worries about a lack of self-sufficiency among the able-bodied poor, and are embracing new limitations on the program for both fiscal and political reasons.
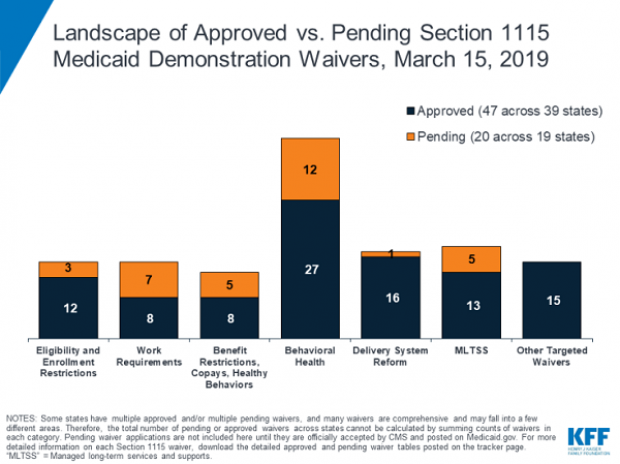
In 2017, the White House in 2017 gave states the green light to explore ways to limit the reach and expense of their Medicaid programs. Governors have proposed a variety of new rules, which require waivers from the federal government to enact. Kentucky, for example, wants to drug-test Medicaid recipients, and Utah wants a partial expansion and a cap on payments. Kaiser Health News summarizes the variety of waivers states have requested, which are governed by Section 1115 of the Social Security Act, in the chart below.
Legal challenges: Efforts to restrict Medicaid have received legal challenges, and U.S. District Judge James Boasberg blocked work requirements in Kentucky last year. The same judge, who has expressed doubts about the administration’s approach to Medicaid, will rule on the legality of work requirements in both Kentucky and Arkansas by April 1.
The bottom line: The Trump administration is seeking fundamental changes in how Medicaid works. Even if Boasberg rules against work requirements, expect the White House and Republican governors to continue to push for new limitations on the program.
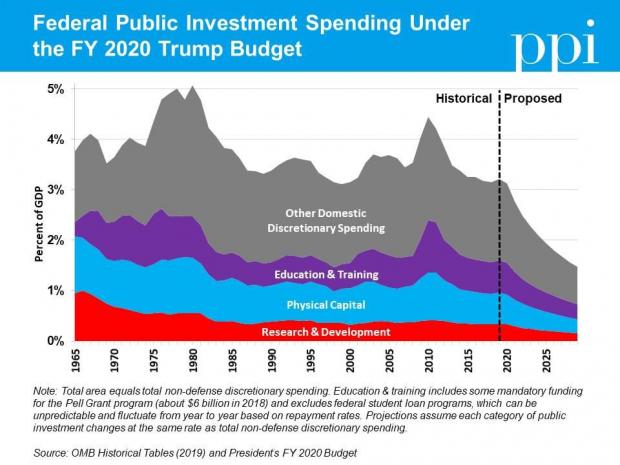
Chart of the Day: Trump's Huge Proposed Cuts to Public Investment

Ben Ritz of the Progressive Policy Institute slams President Trump’s new budget:
“It would dismantle public investments that lay the foundation for economic growth, resulting in less innovation. It would shred the social safety net, resulting in more poverty. It would rip away access to affordable health care, resulting in more disease. It would cut taxes for the rich, resulting in more income inequality. It would bloat the defense budget, resulting in more wasteful spending. And all this would add up to a higher national debt than the policies in President Obama’s final budget proposal.”
Here’s Ritz’s breakdown of Trump’s proposed spending cuts to public investment in areas such as infrastructure, education and scientific research:
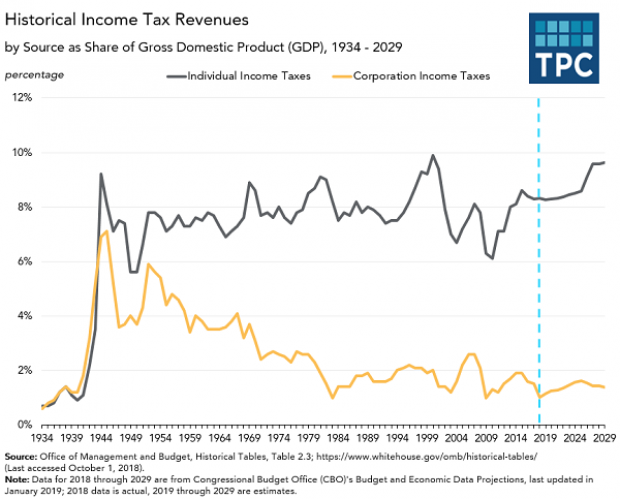
Chart of the Day: The Decline in Corporate Taxes

Since roughly the end of World War Two, individual income taxes in the U.S. have equaled about 8 percent of GDP. By contrast, the Tax Policy Center says, “corporate income tax revenues declined from 6% of GDP in 1950s to under 2% in the 1980s through the Great Recession, and have averaged 1.4% of GDP since then.”