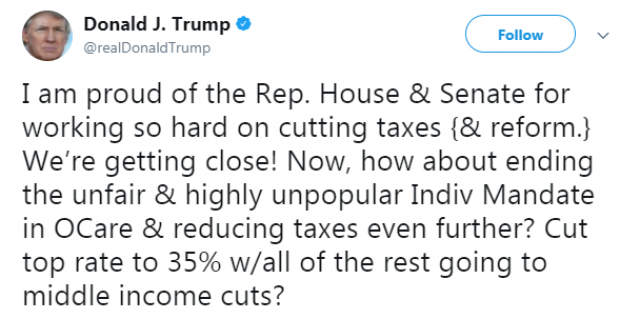Congress Sends Tax Bill to the White House

The Republican-controlled U.S. House of Representatives gave final approval on Wednesday to the biggest overhaul of the U.S. tax code in 30 years, sending a sweeping $1.5 trillion bill to President Donald Trump for his signature.
In sealing Trump’s first major legislative victory, Republicans steamrolled opposition from Democrats to pass a bill that slashes taxes for corporations and the wealthy while giving mixed, temporary tax relief to middle-class Americans.
The House approved the measure, 224-201, passing it for the second time in two days after a procedural foul-up forced another vote on Wednesday. The Senate had passed it 51-48 in the early hours of Wednesday.
Trump had emphasized a tax cut for middle-class Americans during his 2016 campaign. At the beginning of a Cabinet meeting on Wednesday, he said lowering the corporate tax rate from 35 percent to 21 percent was “probably the biggest factor in this plan.”
Trump planned a tax-related celebration with U.S. lawmakers at the White House in the afternoon but will not sign the legislation immediately. The timing of the signing was still up in the air.
After Trump repeatedly urged Republicans to get it to him to sign before the end of the year, White House economic adviser Gary Cohn said the timing of signing the bill depends on whether automatic spending cuts triggered by the legislation could be waived. If so, the president will sign it before the end of the year, he said.
The debt-financed legislation cuts the U.S. corporate income tax rate to 21 percent, gives other business owners a new 20 percent deduction on business income and reshapes how the government taxes multinational corporations along the lines the country’s largest businesses have recommended for years.
Millions of Americans would stop itemizing deductions under the bill, putting tax breaks that incentivize home ownership and charitable donations out of their reach, but also making tax returns somewhat simpler and shorter.
The bill keeps the present number of tax brackets but adjusts many of the rates and income levels for each one. The top tax rate for high earners is reduced. The estate tax on inheritances is changed so far fewer people will pay.
Once signed, taxpayers likely would see the first changes to their paycheck tax withholdings in February. Most households will not see the full effect of the tax plan on their income until they file their 2018 taxes in early 2019.
In two provisions added to secure needed Republican votes, the legislation also allows oil drilling in Alaska’s Arctic National Wildlife Refuge and repeals the key portion of the Obamacare health system that fined people who did not have healthcare insurance.
“We have essentially repealed Obamacare and we’ll come up with something that will be much better,” Trump said on Wednesday.
“Pillaging”
Democrats have called the tax legislation a giveaway to the wealthy that will widen the income gap between rich and poor, while adding $1.5 trillion over the next decade to the $20 trillion national debt, which Trump promised in 2016 he would eliminate as president.
“Today the Republicans take their victory lap for successfully pillaging the American middle class to benefit the powerful and the privileged,” said House Democratic leader Nancy Pelosi.
few Republicans, whose party was once defined by its fiscal hawkishness, have protested the deficit-spending encompassed in the bill. But most of them have voted for it anyway, saying it would help businesses and individuals, while boosting an already expanding economy they see as not growing fast enough.
“We’ve had two quarters in a row of 3 percent growth,” Senate Republican leader Mitch McConnell said after the Senate vote. “The stock market is up. Optimism is high. Coupled with this tax reform, America is ready to start performing as it should have for a number of years.”
Despite Trump administration promises that the tax overhaul would focus on the middle class and not cut taxes for the rich, the nonpartisan Tax Policy Center, a think tank in Washington, estimated middle-income households would see an average tax cut of $900 next year under the bill, while the wealthiest 1 percent of Americans would see an average cut of $51,000.
The House was forced to vote again after the Senate parliamentarian ruled three minor provisions violated arcane Senate rules. To proceed, the Senate deleted the three provisions and then approved the bill.
Because the House and Senate must approve the same legislation before Trump can sign it into law, the Senate’s late Tuesday vote sent the bill back to the House.
Democrats complained the bill was a product of a hurried, often secretive process that ignored them and much of the Republican rank-and-file. No public hearings were held and numerous narrow amendments favored by lobbyists were added late in the process, tilting the package more toward businesses and the wealthy.
U.S. House Speaker Paul Ryan defended the bill in television interviews on Wednesday morning, saying support would grow for after it passes and Americans felt relief.
“I think minds are going to change,” Ryan said on ABC’s “Good Morning America” program.
Reporting by David Morgan and Amanda Becker; Additional reporting by Richard Cowan, Roberta Rampton, Gina Chon and Susan Heavey; Editing by Jeffrey Benkoe and Bill Trott.
Greenspan Has a Warning About the GOP Tax Plan

The Republican tax cuts won’t do much for economic growth, former Federal Reserve Chair Alan Greenspan told CNBC Wednesday, but they will damage the country’s fiscal situation while creating the threat of stagflation. "This is a terrible fiscal situation we've got ourselves into," Greenspan said. "The administration is doing tax cuts and a spending decrease, but he's doing them in the wrong order. What we need right now is to focus totally on reducing the debt."
The US Economy Hits a Sweet Spot

“The U.S. economy is running at its full potential for the first time in a decade, a new milestone for an expansion now in its ninth year,” The Wall Street Journal reports. But the milestone was reached, in part, because the Congressional Budget Office has, over the last 10 years, downgraded its estimate of the economy’s potential output. “Some economists think more slack remains in the job market than October’s 4.1% unemployment rate would suggest. Also, economic output is still well below its potential level based on estimates produced a decade ago by the CBO.”
The New York Times Drums Up Opposition to the Tax Bill

The New York Times editorial board took to Twitter Wednesday “to urge the Senate to reject a tax bill that hurts the middle class & the nation's fiscal health.”
Using the hashtag #thetaxbillshurts, the NYT Opinion account posted phone numbers for Sens. Susan Collins, Bob Corker, Jeff Flake, James Lankford, John McCain, Lisa Murkowski and Jerry Moran. It urged readers to call the senators and encourage them to oppose the bill.
In an editorial published Tuesday night, the Times wrote that “Republican senators have a choice. They can follow the will of their donors and vote to take money from the middle class and give it to the wealthiest people in the world. Or they can vote no, to protect the public and the financial health of the government.”
Like what you're reading? Sign up for our free newsletter.
Can Trump Succeed Where Mnuchin and Cohn Have Flopped?

President Trump met with members of the Senate Finance Committee Monday and is scheduled to attend Senate Republicans’ weekly policy lunch and make a personal push for the tax plan on Tuesday. Will he be a more effective salesman than surrogates in his administration?
Politico’s Annie Karni and Eliana Johnson report that both Democrats and Republicans say Mnuchin and chief economic adviser Gary Cohn have repeatedly botched their tax pitches, “in part due to their own backgrounds” as wealthy Goldman Sachs alums. “House Speaker Paul Ryan earlier this month asked the White House not to send Mnuchin to the Hill to talk with Republican lawmakers about the bill, according to two people familiar with the discussions — though Ryan has praised the Treasury secretary’s ability to improve the legislation itself,” Karni and Johnson write.
Trump: Repeal the Obamacare Mandate to Cut the Top Tax Rate

President Trump repeated his call Monday to repeal the Affordable Care Act’s individual mandate as part of the tax bill. In a tweet — geotagged from Pennsylvania, not the Philippines , where Trump currently is — Trump added that the billions in savings from ending the mandate should be used to cut the top marginal rate to 35 percent and the rest on cuts for the middle class.
The Congressional Budget Office said last week that eliminating the mandate would save $338 billion over the next decade.
The current version of the House tax bill keeps the top individual income tax rate at 39.6 percent, while the Senate bill lowers it to 38.5 percent. However, mandate repeal is not currently part of either tax bill, and, as The New York Times notes, “repeal of the individual mandate was not on the list of 355 amendments that the [Senate Finance Committee] released on Sunday night.”