Congress Sends Tax Bill to the White House

The Republican-controlled U.S. House of Representatives gave final approval on Wednesday to the biggest overhaul of the U.S. tax code in 30 years, sending a sweeping $1.5 trillion bill to President Donald Trump for his signature.
In sealing Trump’s first major legislative victory, Republicans steamrolled opposition from Democrats to pass a bill that slashes taxes for corporations and the wealthy while giving mixed, temporary tax relief to middle-class Americans.
The House approved the measure, 224-201, passing it for the second time in two days after a procedural foul-up forced another vote on Wednesday. The Senate had passed it 51-48 in the early hours of Wednesday.
Trump had emphasized a tax cut for middle-class Americans during his 2016 campaign. At the beginning of a Cabinet meeting on Wednesday, he said lowering the corporate tax rate from 35 percent to 21 percent was “probably the biggest factor in this plan.”
Trump planned a tax-related celebration with U.S. lawmakers at the White House in the afternoon but will not sign the legislation immediately. The timing of the signing was still up in the air.
After Trump repeatedly urged Republicans to get it to him to sign before the end of the year, White House economic adviser Gary Cohn said the timing of signing the bill depends on whether automatic spending cuts triggered by the legislation could be waived. If so, the president will sign it before the end of the year, he said.
The debt-financed legislation cuts the U.S. corporate income tax rate to 21 percent, gives other business owners a new 20 percent deduction on business income and reshapes how the government taxes multinational corporations along the lines the country’s largest businesses have recommended for years.
Millions of Americans would stop itemizing deductions under the bill, putting tax breaks that incentivize home ownership and charitable donations out of their reach, but also making tax returns somewhat simpler and shorter.
The bill keeps the present number of tax brackets but adjusts many of the rates and income levels for each one. The top tax rate for high earners is reduced. The estate tax on inheritances is changed so far fewer people will pay.
Once signed, taxpayers likely would see the first changes to their paycheck tax withholdings in February. Most households will not see the full effect of the tax plan on their income until they file their 2018 taxes in early 2019.
In two provisions added to secure needed Republican votes, the legislation also allows oil drilling in Alaska’s Arctic National Wildlife Refuge and repeals the key portion of the Obamacare health system that fined people who did not have healthcare insurance.
“We have essentially repealed Obamacare and we’ll come up with something that will be much better,” Trump said on Wednesday.
“Pillaging”
Democrats have called the tax legislation a giveaway to the wealthy that will widen the income gap between rich and poor, while adding $1.5 trillion over the next decade to the $20 trillion national debt, which Trump promised in 2016 he would eliminate as president.
“Today the Republicans take their victory lap for successfully pillaging the American middle class to benefit the powerful and the privileged,” said House Democratic leader Nancy Pelosi.
few Republicans, whose party was once defined by its fiscal hawkishness, have protested the deficit-spending encompassed in the bill. But most of them have voted for it anyway, saying it would help businesses and individuals, while boosting an already expanding economy they see as not growing fast enough.
“We’ve had two quarters in a row of 3 percent growth,” Senate Republican leader Mitch McConnell said after the Senate vote. “The stock market is up. Optimism is high. Coupled with this tax reform, America is ready to start performing as it should have for a number of years.”
Despite Trump administration promises that the tax overhaul would focus on the middle class and not cut taxes for the rich, the nonpartisan Tax Policy Center, a think tank in Washington, estimated middle-income households would see an average tax cut of $900 next year under the bill, while the wealthiest 1 percent of Americans would see an average cut of $51,000.
The House was forced to vote again after the Senate parliamentarian ruled three minor provisions violated arcane Senate rules. To proceed, the Senate deleted the three provisions and then approved the bill.
Because the House and Senate must approve the same legislation before Trump can sign it into law, the Senate’s late Tuesday vote sent the bill back to the House.
Democrats complained the bill was a product of a hurried, often secretive process that ignored them and much of the Republican rank-and-file. No public hearings were held and numerous narrow amendments favored by lobbyists were added late in the process, tilting the package more toward businesses and the wealthy.
U.S. House Speaker Paul Ryan defended the bill in television interviews on Wednesday morning, saying support would grow for after it passes and Americans felt relief.
“I think minds are going to change,” Ryan said on ABC’s “Good Morning America” program.
Reporting by David Morgan and Amanda Becker; Additional reporting by Richard Cowan, Roberta Rampton, Gina Chon and Susan Heavey; Editing by Jeffrey Benkoe and Bill Trott.
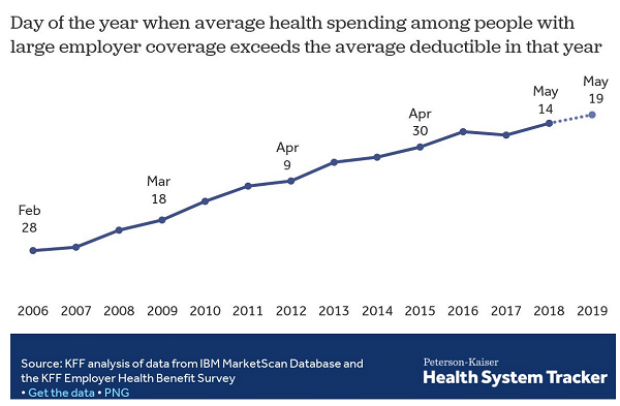
Coming Soon: Deductible Relief Day!

You may be familiar with the concept of Tax Freedom Day – the date on which you have earned enough to pay all of your taxes for the year. Focusing on a different kind of financial burden, analysts at the Kaiser Family Foundation have created Deductible Relief Day – the date on which people in employer-sponsored insurance plans have spent enough on health care to meet the average annual deductible.
Average deductibles have more than tripled over the last decade, forcing people to spend more out of pocket each year. As a result, Deductible Relief Day is “getting later and later in the year,” Kaiser’s Larry Levitt said in a tweet Thursday.
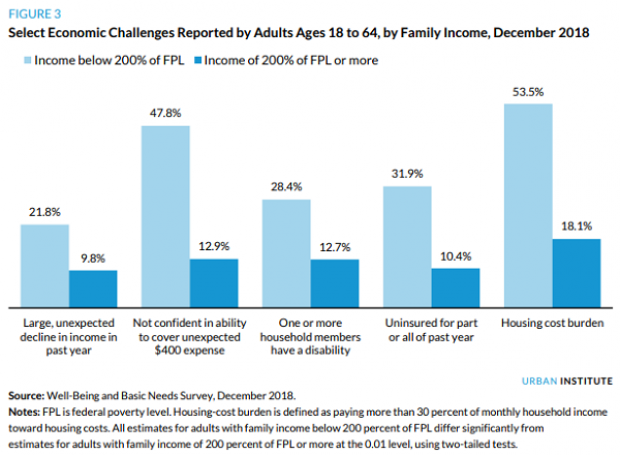
Chart of the Day: Families Still Struggling

Ten years into what will soon be the longest economic expansion in U.S. history, 40% of families say they are still struggling, according to a new report from the Urban Institute. “Nearly 4 in 10 nonelderly adults reported that in 2018, their families experienced material hardship—defined as trouble paying or being unable to pay for housing, utilities, food, or medical care at some point during the year—which was not significantly different from the share reporting these difficulties for the previous year,” the report says. “Among adults in families with incomes below twice the federal poverty level (FPL), over 60 percent reported at least one type of material hardship in 2018.”
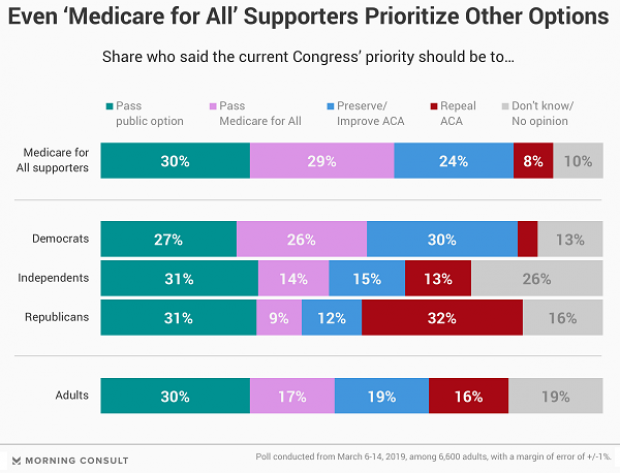
Chart of the Day: Pragmatism on a Public Option

A recent Morning Consult poll 3,073 U.S. adults who say they support Medicare for All shows that they are just as likely to back a public option that would allow Americans to buy into Medicare or Medicaid without eliminating private health insurance. “The data suggests that, in spite of the fervor for expanding health coverage, a majority of Medicare for All supporters, like all Americans, are leaning into their pragmatism in response to the current political climate — one which has left many skeptical that Capitol Hill can jolt into action on an ambitious proposal like Medicare for All quickly enough to wrangle the soaring costs of health care,” Morning Consult said.
Chart of the Day: The Explosive Growth of the EITC

The Earned Income Tax Credit, a refundable tax credit for low- to moderate-income workers, was established in 1975, with nominal claims of about $1.2 billion ($5.6 billion in 2016 dollars) in its first year. According to the Tax Policy Center, by 2016 “the total was $66.7 billion, almost 12 times larger in real terms.”
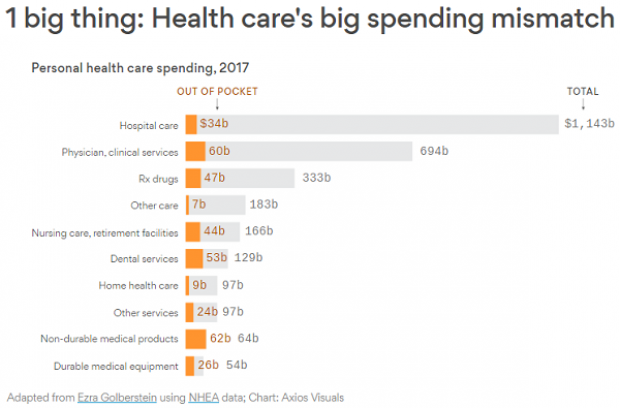
Chart of the Day: The Big Picture on Health Care Costs

“The health care services that rack up the highest out-of-pocket costs for patients aren't the same ones that cost the most to the health care system overall,” says Axios’s Caitlin Owens. That may distort our view of how the system works and how best to fix it. For example, Americans spend more out-of-pocket on dental services ($53 billion) than they do on hospital care ($34 billion), but the latter is a much larger part of national health care spending as a whole.