Republicans Push Ahead on Medicaid Restrictions

The Trump administration on Friday approved Ohio’s request to impose work requirements on Medicaid recipients. Starting in 2021, the state will require most able-bodied adults aged 19 to 49 to either work, go to school, be in job training or volunteer for 80 hours a month in order to receive Medicaid benefits. Those who fail to meet the requirements over 60 days will be removed from the system, although they can reapply immediately.
The new work requirements include exemptions for pregnant women, caretakers and those living in counties with high unemployment rates and will apply only to those covered through the expansion of Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act. There are currently about 540,000 people on Medicaid in Ohio who receive coverage through the expansion, according to Kaitlin Schroeder of The Dayton Daily News, compared to roughly 2.6 million Medicaid recipients in the state overall.
Once implemented, the work requirements are expected to result in 36,000 people losing their Medicaid eligibility, according to state officials, though critics say the reductions could be significantly larger. Similar work requirements in Arkansas pushed 18,000 people off the Medicaid rolls in six months.
A larger GOP project: The creation of new work requirements is part of a larger effort by Republicans to limit the expansion of Medicaid, says The Wall Street Journal’s Stephanie Armour. Since the Affordable Care Act passed in 2010, 36 states have expanded their Medicaid programs under the ACA and the number of people in the program has grown by 50 percent, from roughly 50 million to about 75 million. But many red-state governors have expressed concerns about the cost of Medicaid expansion and worries about a lack of self-sufficiency among the able-bodied poor, and are embracing new limitations on the program for both fiscal and political reasons.
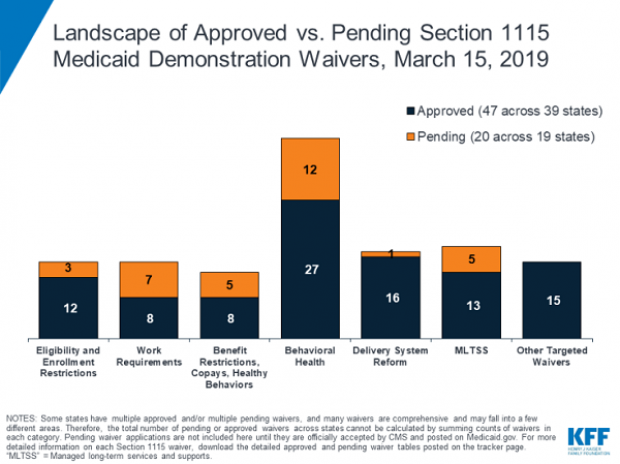
In 2017, the White House in 2017 gave states the green light to explore ways to limit the reach and expense of their Medicaid programs. Governors have proposed a variety of new rules, which require waivers from the federal government to enact. Kentucky, for example, wants to drug-test Medicaid recipients, and Utah wants a partial expansion and a cap on payments. Kaiser Health News summarizes the variety of waivers states have requested, which are governed by Section 1115 of the Social Security Act, in the chart below.
Legal challenges: Efforts to restrict Medicaid have received legal challenges, and U.S. District Judge James Boasberg blocked work requirements in Kentucky last year. The same judge, who has expressed doubts about the administration’s approach to Medicaid, will rule on the legality of work requirements in both Kentucky and Arkansas by April 1.
The bottom line: The Trump administration is seeking fundamental changes in how Medicaid works. Even if Boasberg rules against work requirements, expect the White House and Republican governors to continue to push for new limitations on the program.
Photo of the Day: Kanye West at the White House

This is 2018: Kanye West visited President Trump at the White House Thursday and made a rambling 10-minute statement that aired on TV news networks. West’s lunch with the president was supposed to focus on clemency, crime in his hometown of Chicago and economic investment in urban areas, but his Oval Office rant veered into the bizarre. And since this is the world we live in, we’ll also point out that West apparently became “the first person to ever publicly say 'mother-f***er' in the Oval Office.”
Trump called Kanye’s monologue “pretty impressive.”
“That was bonkers,” MSNBC’s Ali Velshi said afterward.
Again, this is 2018.
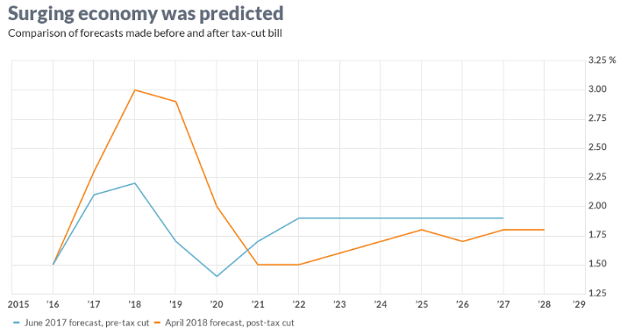
Chart of the Day: GDP Growth Before and After the Tax Bill

President Trump and the rest of the GOP are celebrating the recent burst in economic growth in the wake of the tax cuts, with the president claiming that it’s unprecedented and defies what the experts were predicting just a year ago. But Rex Nutting of MarketWatch points out that elevated growth rates over a few quarters have been seen plenty of times in recent years, and the extra growth generated by the Republican tax cuts was predicted by most economists, including those at the Congressional Budget Office, whose revised projections are shown below.
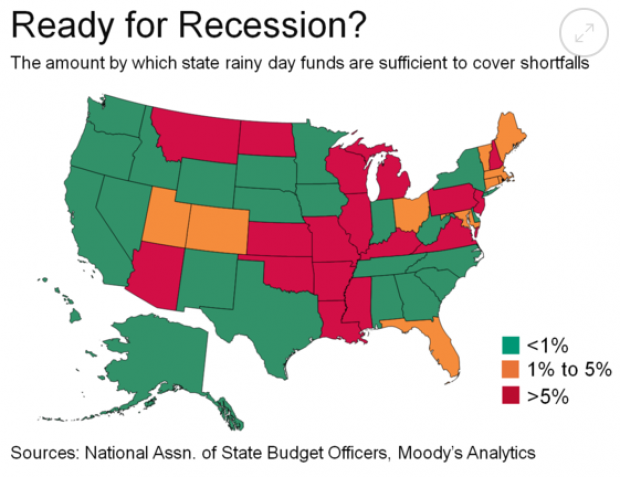
Are States Ready for the Next Downturn?

The Great Recession hit state budgets hard, but nearly half are now prepared to weather the next modest downturn. Moody’s Analytics says that 23 states have enough reserves to meet budget shortfalls in a moderate economic contraction, up from just 16 last year, Bloomberg reports. Another 10 states are close. The map below shows which states are within 1 percent of their funding needs for their rainy day funds (in green) and which states are falling short.
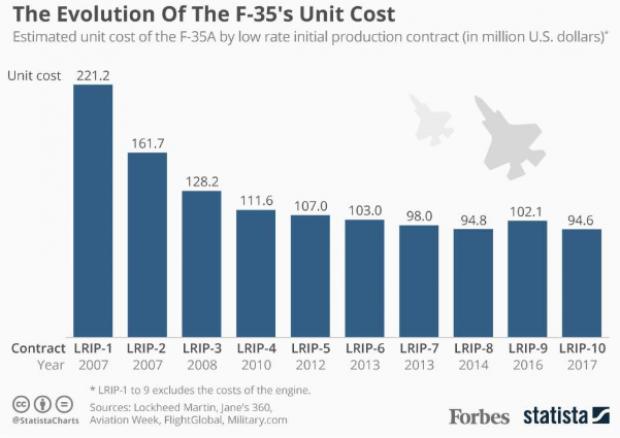
Chart of the Day: Evolving Price of the F-35

The 2019 National Defense Authorization Act signed in August included 77 F-35 Lightning II jets for the Defense Department, but Congress decided to bump up that number in the defense spending bill finalized this week, for a total of 93 in the next fiscal year – 16 more than requested by the Pentagon. Here’s a look from Forbes at the evolving per unit cost of the stealth jet, which is expected to eventually fall to roughly $80 million when full-rate production begins in the next few years.
Wages Are Finally Going Up, Sort of

Average hourly earnings last month rose by 2.9 percent from a year earlier, the Labor Department said Friday — the fastest wage growth since the recession ended in 2009. The economy added 201,000 jobs in August, marking the 95th straight month of gains, while the unemployment rate held steady at 3.9 percent.
Analysts noted, though, that the welcome wage gains merely kept pace with a leading measure of inflation, meaning that pay increases are largely or entirely being canceled out by higher prices. “The last time unemployment was this low, during the dot-com boom, wage growth was significantly faster — well above 3.5 percent,” The Washington Post’s Heather Long wrote. The White House Council of Economic Advisers this week issued a report arguing that wage gains over the past year have been better than they appear in official statistics.